Banff-Kidney-2023-2
Abstract: The Banff Classification of Transplant Pathology is the international consensus classification for the pathology reporting of biopsies from solid organ transplants. Since its initial conception in 1991 for renal transplants, it has undergone constant refinement, reflected in related Banff meeting reports. The rapid expansion of knowledge in the field has led to numerous revisions of the classification. The resultant dispersal of relevant content makes it challenging for pathologists and clinicians to effectively apply the most current classification in routine practice and in clinical trials. This website serves as the most current and comprehensive version of the Banff classification for Renal Transplant Pathology and represents a concise reference document which supersedes all previous Banff meeting reports and is intended as the reference guide for pathologists and clinicians, providing definitions, Banff Lesion Scores, Additional Diagnostic Parameters and Banff Diagnostic Categories. Going forward, this online resource will be up-dated on a regular basis as new knowledge emerges from the work of the international Banff community for Transplant Pathology.
INTRODUCTION
Since its first consensus meeting in 1991,1 the Banff Classification Of Transplant Pathology has provided a framework for the reporting of renal transplant biopsies. It was the first classification system of its kind and answered the need for an international consensus on renal transplant biopsy reporting, providing guidance for clinical diagnosis and enabling meaningful comparison between research studies and clinical trials investigating the diagnosis, treatment and outcome in kidney transplantation. The Banff Classification has since been further strengthened by evidence-informed biannual updates elaborated during open international expert meetings.2 As a result, the Banff Classification of Transplant Pathology has become the predominant classification system used worldwide.3 A total of 16 meetings with changes to the classification reported in 11 articles reflect the developments of the Banff Classification from the first consensus meeting in 1991 to the recently published consensus after the 2022 meeting in Banff, Canada.1,4-14 Each of these iterations provides a short summary of the meeting and contributes to the classification in a cumulative fashion. The dispersal of both relevant and outdated content over 11 articles could make access to the Banff Classification difficult for beginners and experts and has created ambiguities in the past.3 Yet, accessibility and clarity are of utmost importance not only for clinical practice and research but also for the Banff Classification itself to evolve through accountability, critique, and change. To improve on these aspects, the Rules and Dissemination Banff Working Group was initiated at the Banff meeting held in Barcelona, Spain in March 2017. With a scope beyond the helpful syllabus provided by the Banff group in the online supplement of the 2015 update11 and incorporating the latest changes introduced in the 2017 update,12 the aim of this Working Group is to collate all current content of the Banff Classification and improve its accessibility. A systematic inventory of the content is given in Figure 1.
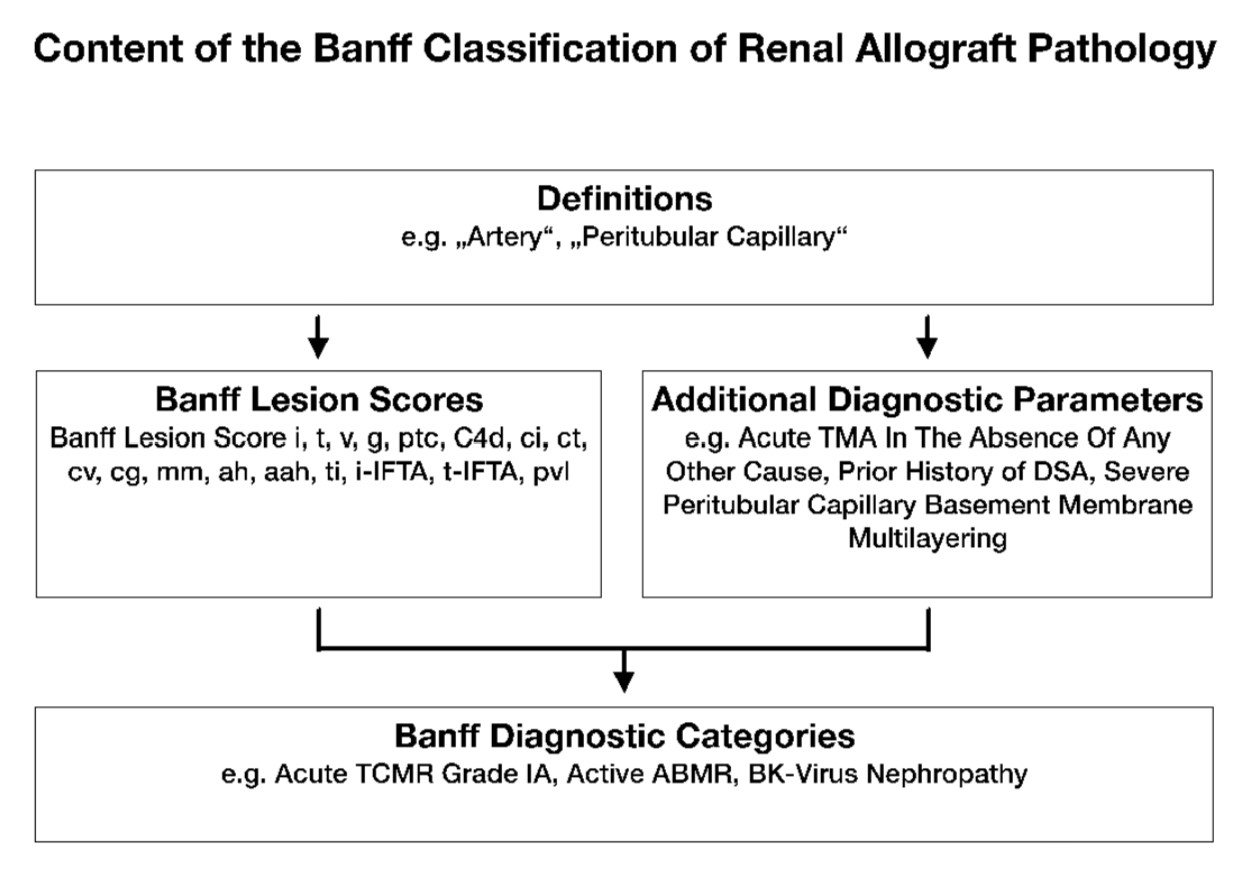
Figure 1. The content of the Banff Classification of Kidney Transplant Pathology can be inventoried as Banff Lesion Scores and Additional Diagnostic Parameters required by the algorithms behind the Banff Diagnostic Categories to reach a diagnosis. Moreover, overarching definitions are important and inform, for example, how one or even several Banff Lesion Scores are applied. TMA, thrombotic microangiopathy.
This practical guide is based on the 2018 review, updated with the changes introduced in the 2019 and 2022 meeting reports. The content of this on-line document is divided into the following sections: a brief guide about the histopathological and serological work-up; a list of Banff Lesion Scores (previously known as components, e.g. Banff t for tubulitis) with their current definitions; practical tips for their application and illustrative figures (see definitions below, thresholds in Table 1 and all Figures); and a list of the Additional Diagnostic Parameters in Table 2. We provide in Table 3 the Banff Diagnostic Categories and the underlying algorithms. A glossary of terms is provided in the appendix below, explaining important concepts and terminology underlying the Banff Classification. Lastly, we provide a critical appraisal of areas of the Banff Classification that require clarification and provide an outlook for future developments. All terms from the Banff Classification will be given in capitals for clarity. All abbreviations for Banff lesion scores will be given in italic typeface. We hope this Banff 101 will serve as a handy reference for the clinicians and the pathologists. Updated content will appear online with the next update of the Banff Classification of Renal Transplant Pathology.
DIAGNOSTIC WORK-UP OF BIOPSIES
A kidney transplant biopsy should fulfil the criteria for specimen adequacy (see Glossary of Terms, in the appendix below) detailed in the Banff 1997 update.5 C4d staining is considered indispensable, either as immunofluorescence (IF) on fresh frozen or immunohistochemistry (IHC) on paraffin-embedded tissue. The paraffin block should be cut in several numbered level sections examined with hematoxylin-eosin, periodic acid-Schiff (PAS), trichrome-elastic and Jones or methenamine silver stains. Immunohistochemistry staining for simian virus-40, cross-reacting with BK virus is highly recommended when indicated. Where available, minute portions of cortex should be embedded for transmission electron microscopy (EM). Depending on clinical and histopathological findings a complete nephropathological work-up including staining for immunoglobulin heavy and light chains and complement split products might be necessary to rule out or confirm a diagnosis of glomerulonephritis. Other ancillary staining might be necessary as for native kidney biopsies to establish specific recurrent or de novo kidney diseases (eg, Congo red stain). Testing for DSA (anti-HLA or other specificity) should be done, following the STAR guidelines.14-17 Detection of non-HLA antibodies (including ABO antibodies in ABO-incompatible transplantation) can be used if the testing protocols are sufficiently standardized and clinically validated for the appropriate clinical context. At present, no non-HLA antibodies (apart from ABO antibodies) have been validated sufficiently for inclusion into the routine clinical classification of kidney transplant biopsies. Ancillary molecular tests, based on tissue and body fluids, are emerging.
Preimplantation biopsies should be obtained, processed, and reported as described by the Banff Working Group on Preimplantation Biopsies.18
BANFF LESION SCORES
Banff Lesion Scores assess the presence and the degree of histopathological changes in the different compartments of renal transplant biopsies, focusing primarily but not exclusively on the diagnostic features seen in rejection. These Banff Lesion Scores are not by themselves sufficient to reach the various Banff Diagnostic Categories in Table 1; the Additional Diagnostic Parameters—histopathological, molecular, serological and/or clinical—may be required to determine the diagnosis. For each Banff Lesion Score we give the current consensus definitions below. As new knowledge emerges, these might be refined for the next Banff update. A synopsis of their semiquantitative thresholds is given in Table 1. However, use of this threshold table without knowledge of the precise definitions and regulatory statutes underlying each Banff Lesion Score is strongly discouraged.
Banff Lesion Score i (Interstitial Inflammation)
This score evaluates the degree of inflammation in non-scarred areas of cortex, which is often a marker of Acute T Cell–Mediated Rejection (TCMR). As per the Banff update from 1997, areas that must not be considered for Banff Lesion Score i are “fibrotic areas, the immediate subcapsular cortex, and the adventitia around large veins and lymphatics”.5 As can indirectly be derived from the definition of Banff Lesion Score ti in the 2007 update of the Banff classification, nodular infiltrates, if in unscarred cortex, are also8 considered for Banff Lesion Score i. An asterisk shall be added to Banff Lesion Score i (e.g., i1*), “if there are more than 5% to 10% of eosinophils, neutrophils or plasma cells”.5 Exemplary lesions are shown in Figure 2.
i0—No inflammation or in less than 10% of unscarred cortical parenchyma.
i1—Inflammation in 10 to 25% of unscarred cortical parenchyma.
i2—Inflammation in 26 to 50% of unscarred cortical parenchyma.
i3—Inflammation in more than 50% of unscarred cortical parenchyma.11
Figure 2. Banff Lesion Score i (interstitial Inflammation in non-scarred areas of the cortex). A, Interstitial inflammation in non-scarred areas of the cortex. This Banff Lesion Score, often a marker of TCMR, ranges from 0 to 3, based on the percentage of non-scarred cortex involved, and is usually dominated by mononuclear cells in the case of Acute TCMR. Note the contrast between the non-infiltrated interstitium in the right half of the micrograph and the infiltrate in the edema between the tubules on the left (long arrow). PAS, original magnification x400. B, An example of plasma cell rich interstitial inflammation. If the infiltrate comprises more than 5% to 10% of either eosinophils, neutrophils or plasma cells an asterisk is added to the Banff Lesion Score i (e.g. i1*). H&E, hematoxylin and eosin, original magnification x400.
Banff Lesion Score t (Tubulitis)
This Banff Lesion Score evaluates the degree of inflammation within the epithelium of the cortical tubules. As per the Banff 2003 update “Tubulitis—the presence of mononuclear cells in the basolateral aspect of the renal tubule epithelium” is one of the defining lesion of TCMR in kidney transplants.6 According to Banff 1997, in tubules cut longitudinally, the score shall be determined as the number of mononuclear cells per 10 tubular epithelial cells, which is the average number of epithelial cells per tubular cross-section (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Banff Lesion Score t (tubulitis) in non-atrophic or mildly atrophic tubules. These images display various degrees of tubulitis which is characterized by the presence of mononuclear cells on the basolateral aspect of the tubular epithelial cells, within the confines of the basement membrane. Mononuclear cells (long and short arrows) are noticeable by their characteristic halo and smaller nucleus and more condensed chromatin compared to tubular epithelial cells. A, Banff Lesion Score t0—Cortical tubules without tubulitis which would be scored as t0. H&E, original magnification x200. B, Banff Lesion Score t1—defined as foci of 1-4 mononuclear cells (arrows) per tubular cross section or per 10 tubular epithelial cells. PAS, original magnification x400. C, Banff Lesion Score t2—defined as 5 to 10 mononuclear cells per tubular cross section or per 10 epithelial cells (long arrows). Note that the tubule to the left displays mild tubulitis (short arrows), but the most severely affected tubule dictates the score. PAS, original magnification x400. D, Banff Lesion Score t3—defined as foci with >10 mononuclear cells/ tubular cross section. Note that for this particular tubule the denominator is per 10 tubular epithelial cells as this tubule is sectioned longitudinally. PAS, original magnification x400.
Tubulitis must be present in at least 2 foci. We have emphasized this by rephrasing the criteria for Banff Lesion Scores t0-3 below; the most severely affected tubule determines the score.5,11 Please note also that we have returned from the altered definition with “leukocytes” in the Banff 2015 update11 to “mononuclear cells” as given in the 1997 update.5 According to Banff 2019, lesion score t should only be scored in “preserved” areas of cortex, defined as areas without interstitial fibrosis, in non-atrophic, mildly atrophic, and moderately atrophic tubules. An example of tubulitis in various stages of tubular atrophy is shown in Figure 4. When scoring tubulitis in a biopsy, consider also the definition of the t-IFTA lesion score. t-IFTA scores tubulitis in areas of interstitial fibrosis (see below). Tubulitis is never considered for scoring when affecting severely atrophic tubules (see definition of severely atrophic tubules below), either for t of t-iFTA lesion scores.
t0—No mononuclear cells in tubules or single focus of tubulitis only.
t1— 2 or more foci with 1 to 4 mononuclear cells/tubular cross section (or 10 tubular cells) in the most affected tubule of the focus.
t2— 2 or more foci of tubulitis, at least one of those foci with 5 to 10 mononuclear cells/tubular cross section (or 10 tubular cells) in the most affected tubule of the focus.
t3— 2 or more foci of tubulitis, at least one of those foci with >10 mononuclear cells/tubular cross section in the most affected tubule of the focus, or the presence of ≥2 areas of tubular basement membrane destruction accompanied by i2/i3 inflammation and t2 elsewhere. 12
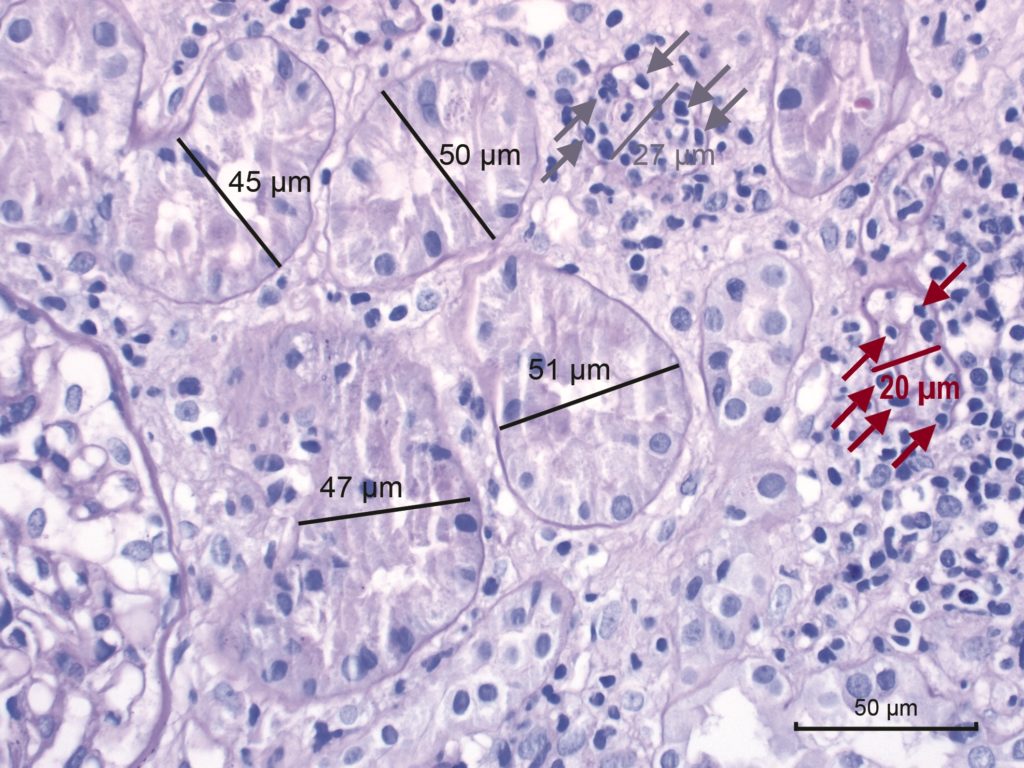 Figure 4. Banff Lesion Score t-IFTA (tubulitis) in moderately atrophic tubules. Moderately atrophic tubules are defined as having less than 50% down to 25% of the diameter of the surrounding “unaffected or minimally affected [cortical] tubules in the biopsy”.12 This example shows such unaffected or minimally affected tubules with their diameter marked in black. Their mean diameter in this image would be around 48 μm. The tubule with the diameter marked in grey has a diameter of 27 μm which is more than 50% of 48 μm. Thus, this tubule would still qualify as mildly atrophic and would inform Banff Lesion Score t if this lesion was found in multiple (at least 2) foci. It is heavily infiltrated with mononuclear cells (grey arrows). In contrast, the tubule with the diameter of 20 μm marked in red is moderately atrophic and in an area of interstitial fibrosis, hence it would inform Banff Lesion score t-IFTA, but not Banff Lesion Score t. PAS, original magnification x400.
Figure 4. Banff Lesion Score t-IFTA (tubulitis) in moderately atrophic tubules. Moderately atrophic tubules are defined as having less than 50% down to 25% of the diameter of the surrounding “unaffected or minimally affected [cortical] tubules in the biopsy”.12 This example shows such unaffected or minimally affected tubules with their diameter marked in black. Their mean diameter in this image would be around 48 μm. The tubule with the diameter marked in grey has a diameter of 27 μm which is more than 50% of 48 μm. Thus, this tubule would still qualify as mildly atrophic and would inform Banff Lesion Score t if this lesion was found in multiple (at least 2) foci. It is heavily infiltrated with mononuclear cells (grey arrows). In contrast, the tubule with the diameter of 20 μm marked in red is moderately atrophic and in an area of interstitial fibrosis, hence it would inform Banff Lesion score t-IFTA, but not Banff Lesion Score t. PAS, original magnification x400.
Banff Lesion Score v (Intimal Arteritis)
This Banff Lesion Score evaluates the presence and the degree of inflammation within the arterial intima. Arteries are defined as having at least 2 layers of smooth muscle cells in the media (Glossary of Terms, see in the appendix below). Note that intimal arteritis (also referred to as endothelialitis and endarteritis) is defined by the presence of inflammatory cells, mainly lymphocytes and monocytes, in the subendothelial space of 1 or more arteries.10 One such cell suffices. Examples of this lesion are shown in Figure 5. Intimal arteritis is a feature seen in both Acute TCMR and Active AMR. For Banff Lesion Score v, the most severely affected artery dictates the score.5 Similar lesions in arterioles are only coded as an asterisk behind the Banff Lesion Score ah and are disregarded for Banff Lesion Score v. Infiltrates buried deeper in the intima are not considered for the v Banff Lesion Score but have been recognized as Chronic Active TCMR since the 2005 update7 and graded in the 2017 update as Grade II.12 In the presence of tubulointerstitial hemorrhage (see Glossary of Terms in the appendix below) and/or and infarct (see Glossary of Terms in the appendix below) an asterisk “*” is attached to the Banff Lesion Score v (e.g. Banff v0*, v2*).5
v0—No arteritis.
v1—Mild to moderate intimal arteritis in at least 1 arterial cross section.
v2—Severe intimal arteritis with at least 25% luminal area lost in at least 1 arterial cross section.
v3—Transmural arteritis and/or arterial fibrinoid change and medial smooth muscle necrosis with lymphocytic infiltrate in vessel.11
Figure 5. Banff Lesion Score v (intimal arteritis). These photomicrographs demonstrate intimal arteritis, characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells beneath the lining endothelial cells. A, Banff Lesion Score v1—mild to moderate arteritis with mononuclear cells (long arrows) immediately beneath lifted endothelial cells (short arrow). H&E, original magnification 200. B, Banff Lesion Score v2—severe intimal arteritis involving over 25% of the arterial lumen with mononuclear cells (long arrows) immediately beneath lifted endothelial cells (short arrow). H&E, original magnification 200; C, Banff Lesion Score v3 -Transmural arteritis with fibrinoid necrosis in the media (long arrow) and mononuclear infiltrate in the arterial wall (short arrows). Intimal arteritis can be seen in both Acute TCMR Grade II and III and Active AMR. The most severely affected artery determines the score. Masson trichrome, original magnification 100. D, this image demonstrates an area of interstitial hemorrhage characterized by extravasation of red blood cells into the surrounding interstitium (arrow). Although there is not a specific Banff Lesion Score for this feature, it can be recorded by attaching an asterisk to the v score (e.g. v*). Note that this asterisk attached to Banff Lesion Score v is not specific for interstitial hemorrhage as an area of cortical infarct (not shown) would also be coded like this. H&E, original magnification x400.
Banff Lesion Score g (Glomerulitis)
This Banff Lesion Score evaluates the degree of inflammation within glomeruli (Figure 6). Glomerulitis is a form of microvascular inflammation (MVI) and is a feature of activity and antibody interaction with tissue in AMR. It can also be seen in recurrent or de novo glomerulonephritis which must be excluded by appropriate immunostains and EM. Banff Lesion Score g is determined by the proportion of glomeruli showing glomerulitis defined as “complete or partial occlusion of 1 or more glomerular capillary by leukocyte infiltration and endothelial cell enlargement.”10 Leukocytes include polymorphonuclear cells and mononuclear cells. Both endothelial cell enlargement and leukocyte(s) must contribute to the complete or partial occlusion. Of note, glomerulitis must be scored even in glomeruli with segmental glomerulosclerosis. The denominator in this proportion is the number of non-sclerosed glomeruli in the biopsy.
g0—No glomerulitis.
g1—Segmental or global glomerulitis in less than 25% of glomeruli.
g2—Segmental or global glomerulitis in 25 to 75% of glomeruli.
g3—Segmental or global glomerulitis in more than 75% of glomeruli.11
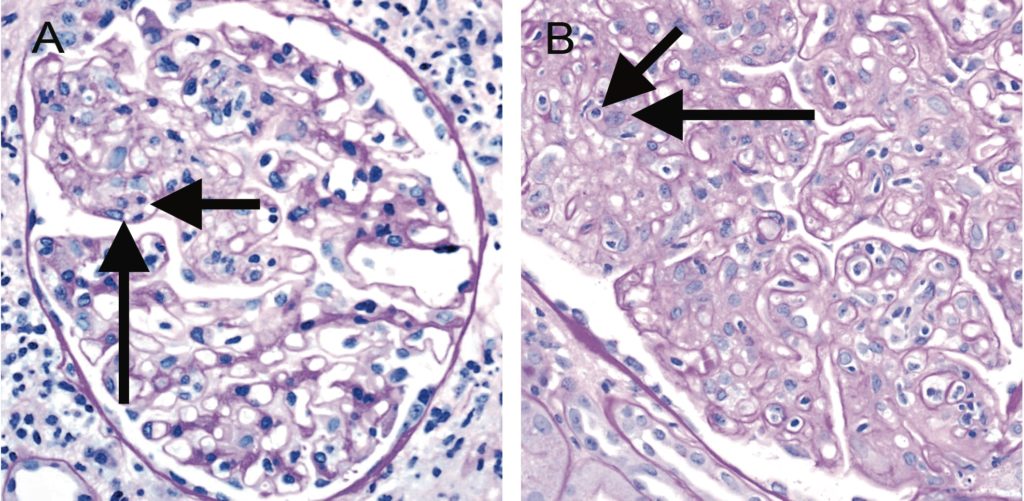 Figure 6. Banff Lesion Score g (glomerulitis). Glomerulitis is a form of MVI and a feature of AMR activity. A, segmental glomerulitis; PAS, original magnification x400. B, Global glomerulitis. Note the characteristic complete or partial occlusion of capillary loops by leukocytes (short arrows) and endothelial cell swelling (long arrows). The score of g0 to g3 is determined by the percentage of glomeruli involved with either segmental or global glomerulitis. Complete or partial occlusion of a single capillary loop suffices to mark the respective glomerulus as involved by the glomerulitis. PAS, original magnification x400.
Figure 6. Banff Lesion Score g (glomerulitis). Glomerulitis is a form of MVI and a feature of AMR activity. A, segmental glomerulitis; PAS, original magnification x400. B, Global glomerulitis. Note the characteristic complete or partial occlusion of capillary loops by leukocytes (short arrows) and endothelial cell swelling (long arrows). The score of g0 to g3 is determined by the percentage of glomeruli involved with either segmental or global glomerulitis. Complete or partial occlusion of a single capillary loop suffices to mark the respective glomerulus as involved by the glomerulitis. PAS, original magnification x400.
Banff Lesion Score ptc (Peritubular Capillaritis)
This Banff Lesion Score evaluates the degree of inflammation within peritubular capillaries (PTCs). Together with glomerulitis, peritubular capillaritis constitutes MVI as a feature of Active AMR or Chronic Active AMR. Peritubular capillaritis can be observed with pure Acute TCMR or Borderline as well. According to the Banff 2005 update, the Banff Lesion Score ptc is determined by the most severely involved PTC (Figure 7). Peritubular capillaries are by definition found in the cortex, their medullary equivalent are medullary vasa recta. The number of luminal inflammatory cells includes polymorphonuclear and mononuclear leukocytes, with an asterisk “*” used to indicate only mononuclear cells and absence of neutrophils. The extent of the PTC inflammation in the biopsy should be documented, either as focal (10-50% of cortical area) or diffuse (>50% of cortical area), but this does not contribute to the score. The presence of associated PTC dilatation may also be noted. Areas affected by acute pyelonephritis or necrosis and subcapsular cortex with nonspecific inflammation should not be scored. Inflammatory cells within PTCs must be distinguished from interstitial inflammation by careful examination of basement membrane stains (PAS, silver). Inflammatory cells within veins and medullary capillaries (vasa recta) should not be scored. Consequently, peritubular capillaritis and Banff Lesion Score ptc can only be assessed in the cortex after exclusion of areas of pyelonephritis and infarcted areas and exclusion of areas close to lymphoid aggregates to avoid confusion with lymphatic vessels. Banff Lesion Score ptc should not be based on longitudinally cut PTCs. Peritubular capillaries in areas affected by tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis must explicitly be considered for this Banff Lesion Score. Note that we have simplified the definition of ptc0 from the original version in the Banff 2017 update.12
ptc0—Maximum number of leukocytes <3.
ptc1—At least 1 leukocyte cell in ≥10% of cortical PTCs with 3-4 leukocytes in most severely involved PTC.
ptc2—At least 1 leukocyte in ≥10% of cortical PTC with 5-10 leukocytes in most severely involved PTC.
ptc3—At least 1 leukocyte in ≥10% of cortical PTC with >10 leukocytes in most severely involved PTC.11

Figure 7. Banff Lesion Score ptc (peritubular capillaritis). Peritubular capillaritis is a form of MVI and a feature of AMR activity and/or antibody interaction with tissue. Each image demonstrates the various ptc Scores which are in themselves determined by the number of inflammatory cells present within capillary lumina. A, Banff Lesion Score ptc1—Mild peritubular capillaritis defined as at least 1 cell in ≥10% of cortical PTCs (short arrows) with 3 to 4 in the most severely involved PTC (long arrow). Please note the slightly distended, open appearance of the capillary which can be a helpful feature; PAS, original magnification x400. B, Banff Lesion Score ptc2—Moderate peritubular capillaritis defined as at least 1 cell in ≥10% of cortical PTCs (short arrows) with 5-10 in most severely involved PTC (long arrow); PAS, original magnification x400. C, Banff Lesion Score ptc3—severe peritubular capillaritis defined as at least 1 cell in ≥10% of cortical PTCs (short arrows) with >10 in most severely involved PTC (long arrow). PAS, original magnification x400. D, this peritubular capillary is cut longitudinally (short arrow) and although containing 4 mononuclear cells is to be disregarded for scoring. However, the neighbouring peritubular capillary (long arrow) is cut orthogonally and would qualify for Banff Lesion Score ptc1 provided that at least 10% of all PTCs contain at least 1 leukocyte. PAS, original magnification x400.
Banff Lesion Score C4d
This score evaluates the extent of staining for C4d on endothelial cells of PTCs and medullary vasa recta by IF on snap frozen sections of fresh tissue or IHC on formalin-fixated and paraffin-embedded tissue. Although Banff 2007 states that areas of tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis have reduced PTC density that could affect the extent of staining,19 scoring of C4d in such cortical areas is not excluded.8 Scoring of C4d staining is based on the percentage of peritubular capillaries and vasa recta that has a linear, circumferential staining pattern (Figure 8). The minimal sample for evaluation is 5 high-power fields of cortex and/or medulla without scarring or infarction. C4d must not be scored in areas of infarction. On IF, staining should be at least 1+ in intensity.8 Strong staining is not required for a positive reading for IHC.11 In terms of extent of staining, with IF, Banff Lesion Score C4d ≥ 2 is considered positive and a criterion for antibody interaction with tissue and as equivalent to DSA (see Table 3 and SDC, Glossary of Terms in the appendix below), whereas with IHC, Banff Lesion Score C4d ≥ 1 is counted as positive already.11 Note that the definition below deviates from the one provided in the Banff 2015 update,11 in that it explicitly allows scoring in medullary vasa recta as originally intended, not only PTCs. The thresholds remain unchanged.
C4d0—No staining of PTC and medullary vasa recta (0%).
C4d1—Minimal C4d staining (>0 but <10% of PTC and medullary vasa recta).
C4d2—Focal C4d staining (10-50% of PTC and medullary vasa recta).
C4d3—Diffuse C4d staining (>50% of PTC and medullary vasa recta).
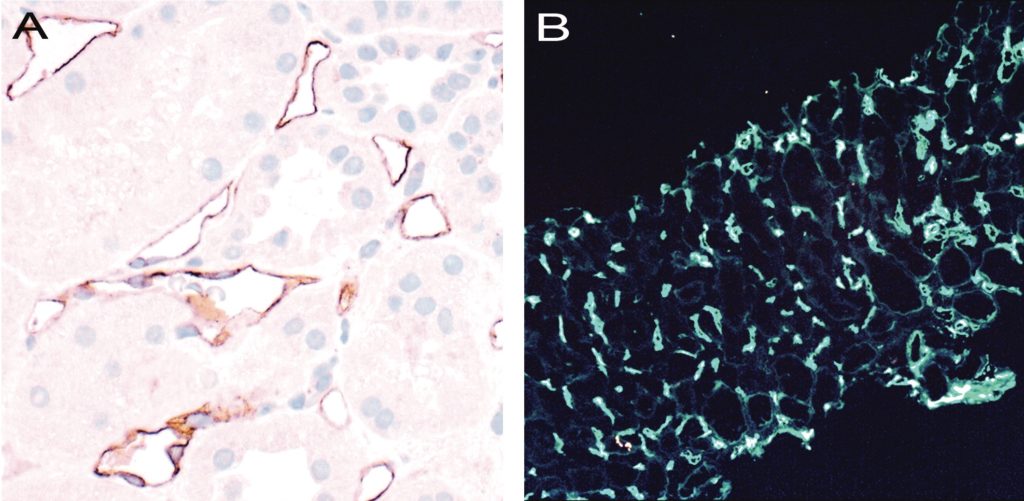
Figure 8. Banff Lesion Score C4d. A, IHC staining with peroxidase yielding a brown reaction product for C4d. An example of C4d3, this image demonstrates linear and circumferential staining of endothelial cells in virtually all peritubular capillaries. The staining was similar in all areas of the cortex and the medulla. The proportion of stained peritubular capillaries and medullary vasa recta informs the score. Immunoperoxidase, original magnification x400 B, IF staining for C4d. This image shows an example of a Banff Lesion Score of C4d3; using IF, a minimum score of C4d ≥ 2 is considered positive. In addition to this, the staining intensity for an individual capillary or medullary vas rectum must be at least 1+ on the usual scale from negative, trace, 1+, 2+ to 3+. Indirect IF, mouse antihuman C4d followed by fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated anti-mouse IgG, original magnification x100.
Banff Lesion Score ci (Interstitial Fibrosis)
This lesion score evaluates the extent of cortical fibrosis. The Banff Classification has never given a precise definition for individual areas of interstitial fibrosis (Figure 9). The reason for this is that Banff Lesion Score ci was meant to purely reflect the cortex composed of fibrous tissue, which does not necessarily correspond to areas that a pathologist would pick up as a patch of pathological tubulointerstitial fibrosis. The fraction of fibrous tissue in the cortex was considered as up to 5% for normal kidneys, whereas any atrophic tubule is considered abnormal, leading to a difference in cut-offs between ci1 and ct1: ci0 allows 0% to 5% of cortical fibrous tissue as normal, whereas ct1 starts anywhere above 0%. A useful definition for interstitial fibrosis proposed at the Banff 2022 meeting was: cortical areas where tubules are not lying back to back, and are separated from each other by fibrous tissue, best appreciated using a silver or trichrome stain. Care should be taken to distinguish separation of tubules by fibrous tissue versus oedema and/or inflammation.

Figure 9. Banff Lesion Scores for ct (tubular atrophy) and ci (interstitial fibrosis). The ci and ct Scores are both based on calculating the total percentage of cortex involved and require a diligent assessment of all foci of ct and ci as this process is often multifocal; ct and ci scores may not always be equally advanced. A, This image demonstrates an area of non-atrophic tubules (long arrow), compared to an area of tubular atrophy (short arrow) without an obvious increase in interstitial fibrosis. PAS, original magnification x200. There are different morphological types of tubular atrophy with differing appearances, including conventional, thyroidization, and endocrine-like types. B, Tubular atrophy of conventional type with interstitial fibrosis. Tubular areas are separated by areas of interstitial fibrosis and tubules show thickened basement membranes and > 50% reduction in tubular diameter (long arrows). PAS, original magnification x200. C, Thyroidization type atrophy. Here, tubules appear dilated, have flattened epithelial cells, and contain eosinophilic and brightly periodic-acid-Schiff-positive uromodulin casts (long arrow). PAS, original magnification x200. D, endocrine-like type, characterized by shrunken tubules with cuboidal epithelium and “tubular simplification” (long arrow). Compared with the other types of tubular atrophy, endocrine-like type does not have thickened basement membranes but still counts toward the ct score. PAS, original magnification x400.
A Working Group on this topic has produced useful reference guides (Figures 10 and 11).20 Of note, determination of Banff Lesion Score ci (as well as Banff Lesion Scores ct, ti, i-IFTA, t-IFTA) must also take into consideration the subcapsular cortex.
ci0—Interstitial fibrosis in up to 5% of cortical area.
ci1—Interstitial fibrosis in 6 to 25% of cortical area (mild interstitial fibrosis).
ci2—Interstitial fibrosis in 26 to 50% of cortical area (moderate interstitial fibrosis).
ci3—Interstitial fibrosis in >50% of cortical area (severe interstitial fibrosis).11
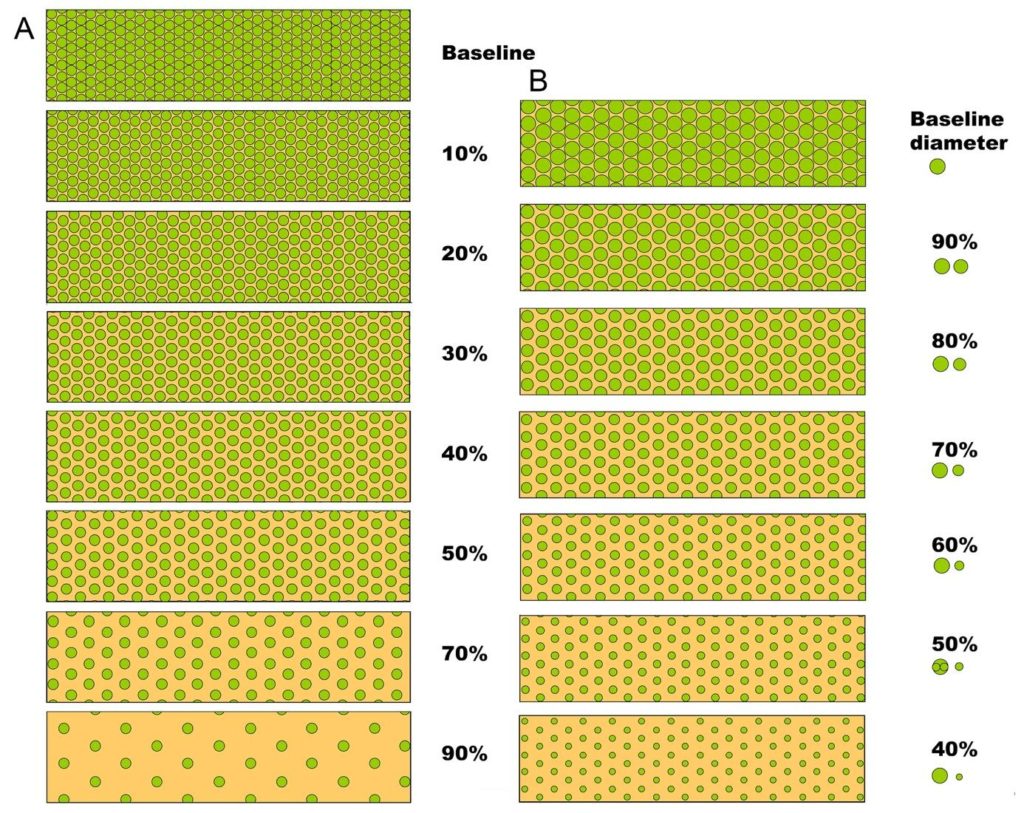
Figure 10. Visual analogue scales provided by the Banff Working Group on Fibrosis. This working group developed schematic diagrams to facilitate and standardize scoring of Banff Lesion Scores ci and ct. A, scale for the assessment of interstitial fibrosis without tubular atrophy. B, scale for the assessment of diffuse tubular atrophy with “replacement fibrosis.”20 Reproduced with kind permission from American Journal of Transplantation.

Figure 11. More visual analogue scales provided by the Banff Working Group on Fibrosis17 A, Scale for the assessment of patchy (left) and confluent (right) interstitial fibrosis without glomeruli. B, Scale for patchy (left) and confluent (right) fibrosis with glomeruli.20 Reproduced with kind permission from American Journal of Transplantation.
Banff Lesion Score ct (Tubular Atrophy)
This Banff Lesion Score evaluates the extent of cortical tubular atrophy which is usually tightly associated with the areas affected with interstitial fibrosis (Figure 9). Both correlate with time posttransplantation in the setting of progressive disease of any cause. Accordingly, neither Banff Lesion Scores ct nor ci have diagnostic specificity, but both have significant correlation with allograft function and prognosis. Historically, the Banff classification has defined tubular atrophy as reflected in the Banff Lesion Score ct in the 1995 update4 as tubules with a thickened basement membrane or a reduction of greater than 50% in tubular diameter. Banff Lesion Score ct is still based on this definition of tubular atrophy. The definitions of moderate and severe atrophy from the Banff 2017 update12 are irrelevant for Banff Lesion Score ct. In the following definition, we have omitted the designation as “mild” for ct1, “moderate” for ct2 and “severe” for ct3 which was still included in the Banff 2015 update to avoid confusion between the definition of atrophy for an individual tubule as described above and the extent of tubular atrophy reflected in the Banff Lesion Score ct. Of note, Banff Lesion Score ct must be determined including the subcapsular cortex.
ct0—No tubular atrophy (defined as tubules with a thickened basement membrane or a reduction of greater than 50% in tubular diameter).
ct1—Tubular atrophy (see ct0) involving up to 25% of the area of cortical tubules.
ct2—Tubular atrophy (see ct0) involving 26 to 50% of the area of cortical tubules.
ct3—Tubular atrophy (see ct0) involving in >50% of the area of cortical tubules.11
Banff Lesion Score cv (Vascular Fibrous Intimal Thickening)
This Banff Lesion Score reflects the extent of arterial intimal thickening in the most severely affected artery (see Definition of Terms in the appendix below), not the average of all arteries.5 It does not discriminate between bland arterial intimal fibrosis and fibrosis containing leukocytes (Figure 12), although the latter is more likely to reflect chronic rejection (AMR and/or Chronic Active TCMR Grade II).12 A visual analogue scale for application in daily practice is provided in Figure 13.
cv0—No chronic vascular changes.
cv1—Vascular narrowing of up to 25% luminal area by fibrointimal thickening.
cv2—Vascular narrowing of 26 to 50% luminal area by fibrointimal thickening.
cv3—Vascular narrowing of more than 50% luminal area by fibrointimal thickening.11
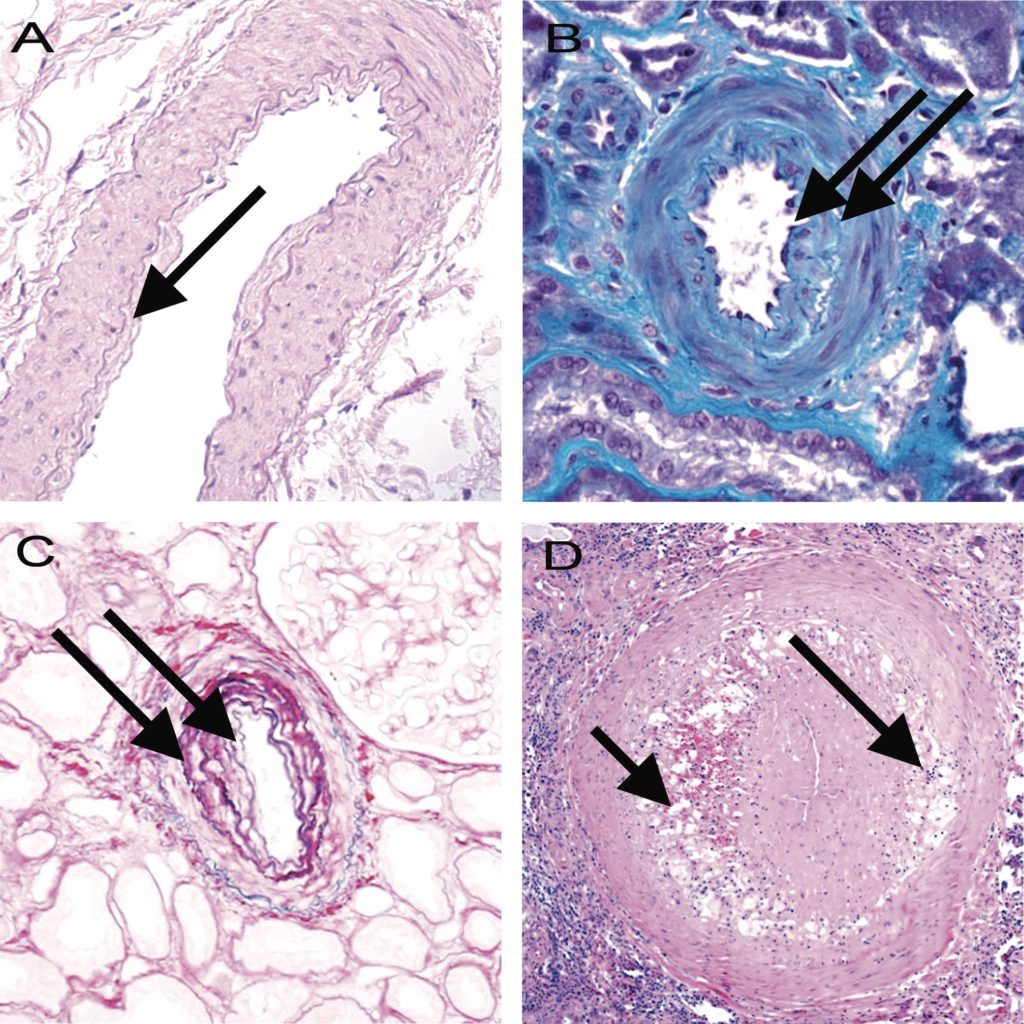
Figure 12. Banff Lesion Score cv (vascular fibrous intimal thickening). A, Banff Lesion Score cv1—very mild purely fibrous thickening of the arterial intima (arrow). PAS, original magnification x200. B, Purely fibrous intimal thickening is depicted here in between the arrows in a trichrome stain. Note that this type of fibrous intimal thickening can also represent chronic damage in AMR. Masson trichrome, original magnification x400. C, Arterial fibrous intimal thickening in between the arrows. Note the multiplication of the internal elastic lamina. Trichrome-elastica, original magnification x400. D, Severe fibrointimal thickening cv3, with mononuclear infiltrates (long arrow) and foam cells (short arrow) in the fibrotic intima which can be a feature of both Chronic Active TCMR and Chronic Active AMR. Both types of lesion qualify for Banff Lesion Score cv, the score is determined by the loss of luminal area as shown in Figure 13 below. H&E, original magnification x100.
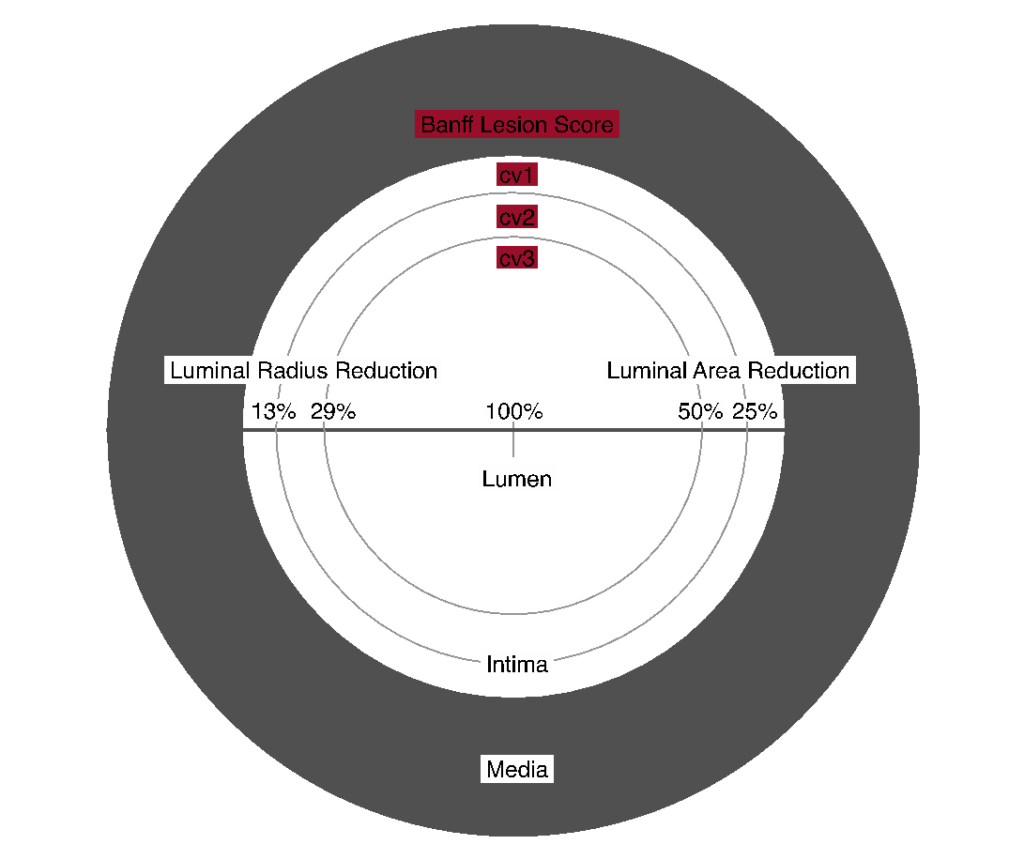 Figure 13. Visual analogue scale for the determination of Banff Lesion Score cv (arterial fibrous intimal thickening). The remaining luminal area is related to the square of the remaining luminal radius. Thus, relatively modest decreases in luminal radius of 13% or 29% translate into relatively large reductions in luminal area of 25% or 50%, reflecting the thresholds for Banff Lesion Score cv.
Figure 13. Visual analogue scale for the determination of Banff Lesion Score cv (arterial fibrous intimal thickening). The remaining luminal area is related to the square of the remaining luminal radius. Thus, relatively modest decreases in luminal radius of 13% or 29% translate into relatively large reductions in luminal area of 25% or 50%, reflecting the thresholds for Banff Lesion Score cv.
Banff cg Score (Glomerular Basement Membrane Double Contours)
Banff Lesion Score cg is based on the presence and extent of glomerular basement membrane (GBM) double contours or multilamination in the most severely affected glomerulus (Figure 14). Scoring should be carried out on PAS or silver stains; a designation as cg1a requires transmission EM to exclude cg0. With Banff Lesion Score cg > 0 (including both cg1a and cg1b), a diagnosis of transplant glomerulopathy (TG) (see Glossary of Terms in the appendix below) can be made, if other causes can be excluded. Banff Lesion Score cg > 0 can be a feature of Chronic AMR or Chronic Active AMR, but can also be seen in association with thrombotic microangiopathy of other causes than AMR, e.g. hepatitis C virus infection,21 hypertensive glomerulopathy,22 and glomerulonephritis. In analogy to Banff Lesion Score g, even in the presence of an explanation other than rejection for GBM double contours, Banff Lesion Score cg shall still be applied. Of note, Banff Lesion Score cg is not scored in ischemic or segmentally sclerosed glomeruli.1,11 Late ischemic glomerulopathy is defined as “thickening, wrinkling and collapse of glomerular capillary walls associated with or extracapillary fibrotic material”.1 As stated above, the earliest lesion of TG (cg1a) requires transmission EM for diagnosis. To detect such lesions, it is recommended that at centers with EM capability, “ultrastructural studies should be performed in all biopsies from patients who are sensitized, have documented DSA at any time post-transplantation and/or who have had a prior biopsy showing C4d staining, glomerulitis and/or peritubular capillaritis”. It is also advised that EM be considered in all biopsies performed from 6 months post-transplantation onward and in for-cause biopsies done from 3 months post-transplantation onward to determine if early changes of TG are present, prompting testing for DSA.10 Electron microscopy is also recommended for any biopsy done for the indication of increasing or new onset proteinuria.
cg0—No GBM double contours by light microscopy (LM) or EM.
cg1a—No GBM double contours by LM but GBM double contours (incomplete or circumferential) in at least 3 glomerular capillaries by EM, with associated endothelial swelling and/or subendothelial electron-lucent widening.
cg1b—Double contours of the GBM in 1-25% of capillary loops in the most affected nonsclerotic glomerulus by LM; EM confirmation is recommended if EM is available.
cg2—Double contours affecting 26 to 50% of peripheral capillary loops in the most affected nonsclerotic glomerulus.
cg3—Double contours affecting more than 50% of peripheral capillary loops in the most affected nonsclerotic glomerulus.11
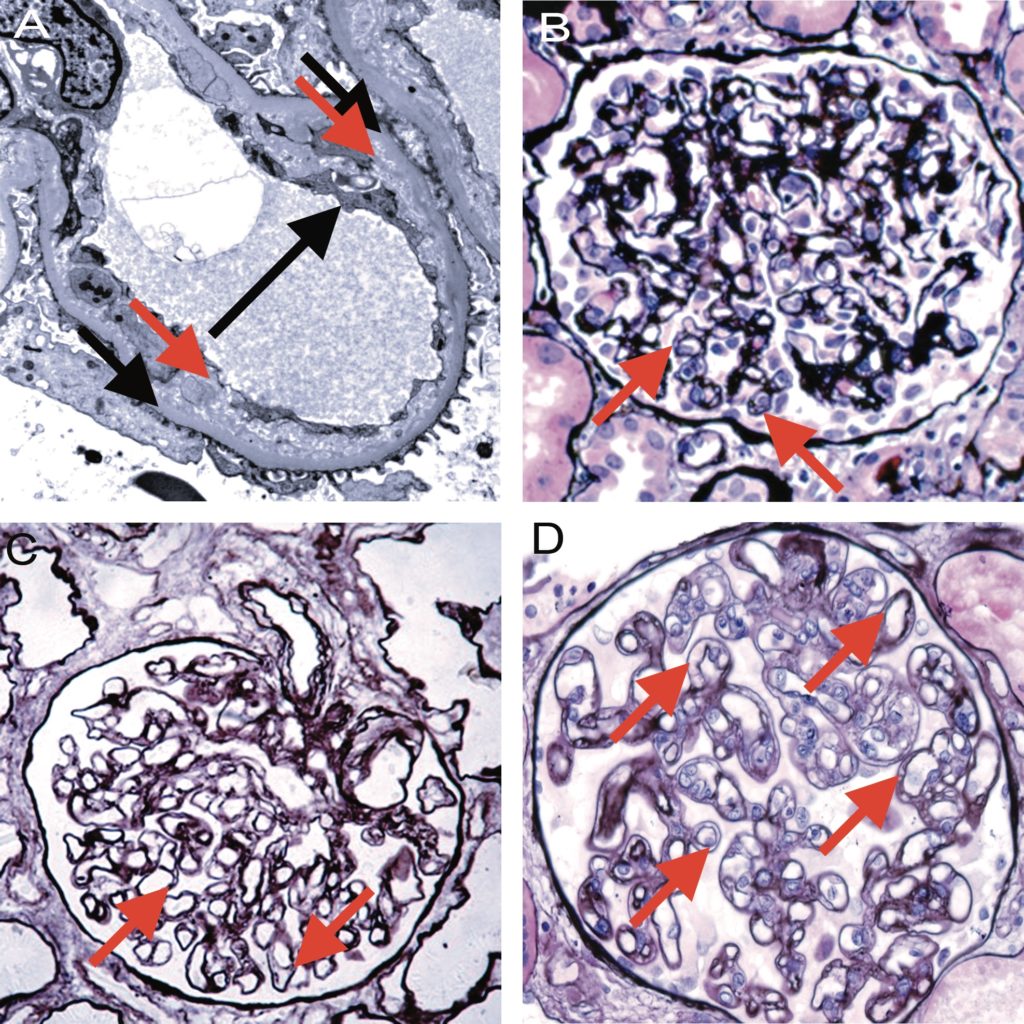
Figure 14. Banff Lesion Score cg (GBM double contours). This score represents the presence and extent of GBM double contours, a criterion of Group 4 of histologic features of AMR chronicity (see Table 3). The score ranges from 0 to 3 and is based on the percentage of capillary loops with double contours as evident on EM (Banff Lesion Score cg1a) or LM (cg1b to cg3) in the most severely affected glomerulus. A, cg1a—GBM with double contours (short black arrows point to areas of original basement membrane and red arrows point to areas of new basement membrane formation), visible by EM only. Double contours, such as those noted in this image must be accompanied by endothelial cell swelling (long black arrow) and/or subendothelial widening and must involve at least 3 glomerular capillaries by EM for a Score of cg1a. Scores of greater than cg1a are based on light microscopic appearance which can best be examined by silver stains. Transmission EM, original magnification x8,000. B, Banff Lesion Score cg1b—double contours (arrow) identified on LM which involve up to 25% of the capillary loops of this most affected glomerulus. Jones silver stain, original magnification x400. C, Banff Lesion Score cg2—double contours (arrows) present in 26-50% of this most affected glomerulus; Jones silver stain, original magnification x400. D, Banff Lesion Score cg3—double contours (arrows) present in >50% of this most affected glomerulus. Jones silver stain, original magnification x400.
Banff Lesion Score mm (Mesangial Matrix Expansion)
This score evaluates the percentage of glomeruli with “moderate mesangial matrix expansion” in relation to all non-sclerotic glomeruli. Banff 1997 defines moderate mesangial matrix increase as “expansion of the matrix in the mesangial interspace to exceed the width of 2 mesangial cells in the average in at least 2 glomerular lobules”.5 An example is shown in Figure 15. Banff Lesion Score mm is currently not used to reach a Diagnostic Category and is purely descriptive.
mm0—No more than mild mesangial matrix increase in any glomerulus.
mm1—At least moderate mesangial matrix increase in up to 25% of nonsclerotic glomeruli.
mm2—At least moderate mesangial matrix increase in 26% to 50% of nonsclerotic glomeruli.
mm3—At least moderate mesangial matrix increase in >50% of nonsclerotic glomeruli.11
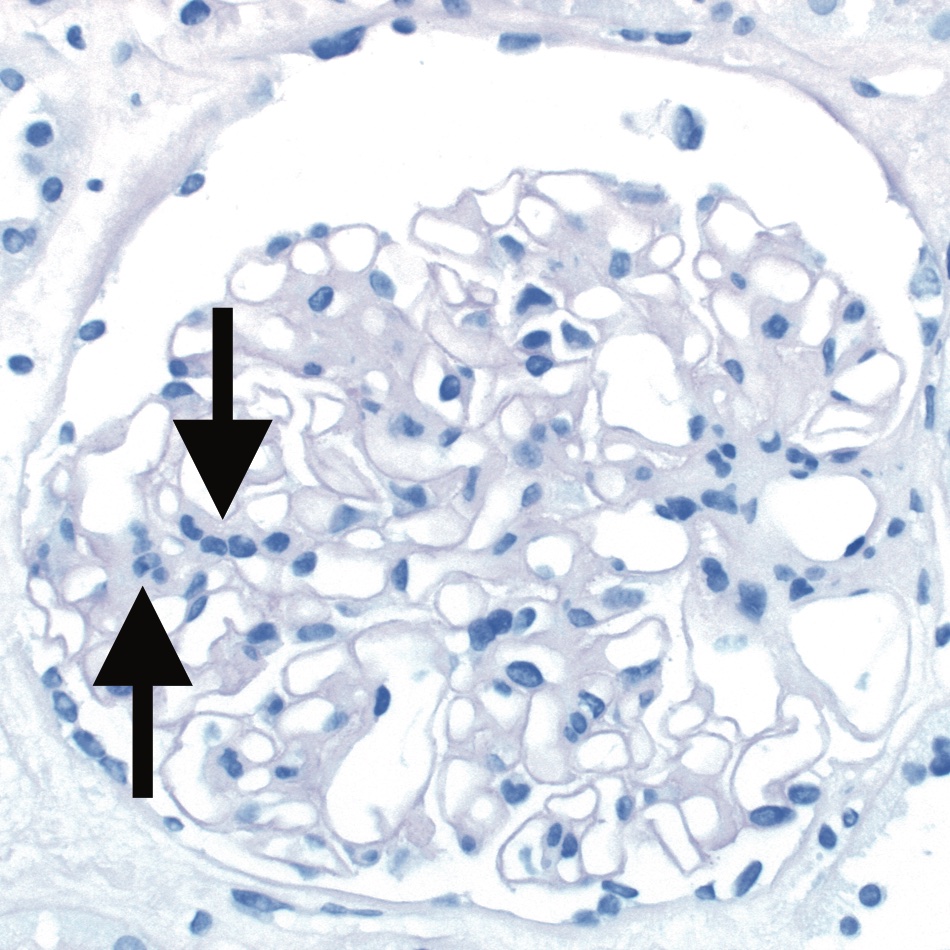
Figure 15. Banff Lesion Score mm (mesangial matrix expansion). This glomerulus fulfils the criteria for moderate mesangial matrix expansion with more than 2 mesangial cells in these 2 adjacent glomerular lobules (arrows). The proportion of glomeruli with such mesangial matrix expansion among all non-sclerosed glomeruli informs the score. The underlying reason for the mesangial matrix expansion in this biopsy was recurrent IgA glomerulonephritis revealed by IHC and EM. PAS, original magnification x400.
Banff Lesion Score ah (Arteriolar Hyalinosis)
This score evaluates the extent of arteriolar hyalinosis (Figure 16). The first edition of the Banff Classification defined ah as “nodular hyaline afferent arteriolar thickening suggestive of cyclosporine toxicity”; however, in Banff 1997 and later updates, Banff Lesion Score ah is defined simply as PAS-positive arteriolar hyaline thickening, as a finding of “uncertain significance”. An asterisk “*” is added to the ah score when arteriolitis is present (e.g. ah0*, ah2*).5 Banff Lesion Score ah is currently not used to reach a diagnostic category and is purely descriptive.
ah0—No PAS (PAS)-positive hyaline arteriolar thickening. ah1—Mild to moderate PAS-positive hyaline thickening in at least 1 arteriole. ah2—Moderate to severe PAS-positive hyaline thickening in more than 1 arteriole. ah3—Severe PAS-positive hyaline thickening in many arterioles.11

Figure 16. Banff Lesion Score ah (arteriolar hyalinosis). A, Banff Lesion Score ah1—mild focal arteriolar hyalinosis (arrow). PAS, original magnification x630. B, ah2—Moderate arteriolar hyalinosis (arrow). PAS, original magnification x630. C, Banff Lesion Score ah2—Note in this image there is both linear (short arrow) and nodular hyalinosis (long arrow). For a score of ah2, more than 1 arteriole displaying moderate to severe is required. Jones silver stain, original magnification x630. D, Banff Lesion Score ah3—severe circumferential arteriolar hyalinosis with luminal occlusion. For Banff Lesion Score ah3, hyalinosis of this severity (arrow) must be present in many arterioles. PAS, original magnification x630.
Banff Lesion Score aah (Hyaline Arteriolar Thickening)
This Banff Lesion Score provides an alternative way of quantifying arteriolar hyalinosis. It was proposed in the 2007 update, because of the insufficient reproducibility of the Banff Lesion Score ah.8 This alternative tries to reach better reproducibility by focusing on circumferential or non-circumferential hyalinosis and the number of involved arterioles. Still, this lesion cannot be considered specific, that is, diagnostic for calcineurin inhibitor-related arteriolopathy. The use of this Banff Lesion Score aah has been left as optional since its introduction in 2007, no final decision has been reached whether it shall replace Banff Lesion Score ah. Banff Lesion Score aah is currently not used to reach a diagnostic category and is purely descriptive. aah0—No typical lesions of calcineurin inhibitor-related arteriolopathy. aah1—Replacement of degenerated smooth muscle cells by hyaline deposits in only 1 arteriole, without circumferential involvement. aah2—Replacement of degenerated smooth muscle cells by hyaline deposits in more than 1 arteriole, without circumferential involvement. aah3—Replacement of degenerated smooth muscle cells by hyaline deposits with circumferential involvement, independent of the number of arterioles involved.11
Banff Lesion Score ti (Total Inflammation)
This lesion score evaluates the extent of total cortical inflammation. According to the Banff 2007 update and in contrast to the Banff Lesion Score i, all of the cortical parenchyma, including areas of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IFTA), subcapsular cortex and perivascular cortex including nodular infiltrates are considered for ti scoring.8 Mengel et al. found Banff Lesion Score ti to be better predictive of poor graft outcomes than the Banff Lesion Score i in cases where at least mild IFTA was present.21 The association between interstitial inflammation in areas of IFTA as reflected in Banff Lesion Score i-IFTA and decreased graft survival was noted by Mannon et al.22 and subsequently confirmed by others.23,24 As a consequence, Banff Lesion Score ti became part of the criteria for a diagnosis of Chronic Active TCMR Grade IA and IB;12 both Banff Lesion Scores ti and i-IFTA must be at least 2 to consider a diagnosis of Chronic Active TCMR Grade IA or IB.12
ti0— No or trivial interstitial inflammation (<10% of total cortical parenchyma).
ti1— 10-25% of total cortical parenchyma inflamed.
ti2— 26-50% of total cortical parenchyma inflamed.
ti3— >50% of total cortical parenchyma inflamed.11

Figure 17. Banff Lesions Score i-IFTA (inflammation in areas of IFTA). Image A shows inflammation in areas of IFTA (arrow). This Lesion Score ranges from 0 to 3, based on the percentage of scarred areas of the cortex (i.e. areas qualifying for ci and ct) involved by inflammation. It is one of the criteria necessary for a diagnosis of Chronic Active TCMR Grade IA or IB. Masson trichrome, original magnification x200. B, In contrast shows interstitial fibrosis without significant infiltrate (arrow). H&E, original magnification x400.
Banff Lesion Score i-IFTA (Inflammation in Area of IFTA)
This score evaluates the extent of inflammation in scarred cortex, i.e. areas that qualify for Banff Lesion Scores ci and ct (Figure 17). The Banff Lesion Score i-IFTA was first introduced to the Banff Classification in 2015.11 Both Banff Lesion Scores ti and i-IFTA must be at least 2 to consider a diagnosis of Chronic Active TCMR Grade IA or IB.12
i-IFTA0—No inflammation or less than 10% of cortical parenchyma with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy.
i-IFTA1—Inflammation in 10% to 25% of cortical parenchyma with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy.
i-IFTA2—Inflammation in 26% to 50% of cortical parenchyma with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy.
i-IFTA3—Inflammation in >50% of cortical parenchyma with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy.11
Banff Lesion Score t-IFTA (Tubulitis in areas of interstitial fibrosis)
This Banff Lesion Score was fully introduced in Banff 2019.13 It refers to scoring of tubulitis in areas of interstitial fibrosis. t-IFTA is graded according to presence of mononuclear cell infiltrates in non-atrophic, mildly atrophic, and moderately atrophic tubules in areas of interstitial fibrosis. Tubulitis in severely atrophic tubules should not be considered. Like for the t lesion score, tubulitis must be present in at least 2 foci. An example is given in Figure 4. Moderately atrophic cortical tubules are those that show a reduction in diameter of more than 50% but are not severely atrophic. Severely atrophic tubules are defined as tubules of diameter <25% of that of unaffected or minimally affected tubules in the biopsy, often with an undifferentiated-appearing, cuboidal or flattened epithelium (or in some cases even loss of epithelium with denudation of the tubular basement membrane), and pronounced wrinkling and/or thickening of the tubular basement membrane. This definition of severely atrophic tubules also includes very small, endocrine-like tubules with very narrow lumens, although the basement membranes of the latter may not be thickened.12 Of note, Banff Lesion Score t-IFTA must be determined including the subcapsular cortex.
t-IFTA0 – no mononuclear cells in tubules in areas of interstitial fibrosis, or single focus of tubulitis only.
t-IFTA1 – 2 or more foci with 1-4 mononuclear cells/tubular cross section (or 10 tubular cells) in the most affected tubule of the focus, in areas of interstitial fibrosis.
t-IFTA2 – 2 or more foci with 5-10 mononuclear cells/tubular cross section (or 10 tubular cells) in the most affected tubule of the focus, in areas of interstitial fibrosis.
t-IFTA3 – 2 or more foci with >10 mononuclear cells/tubular cross section (or 10 tubular cells) in the most affected tubule in the focus, in areas of interstitial fibrosis.
Banff Lesion Score pvl
Developed in the report of the Banff Working Group on Polyomavirus,25 this Banff Lesion Score was formally introduced into the Banff Classification in the 2019 update.13 Banff Lesion Score pvl is determined over the entire biopsy sample (cortex, medulla, scarred or unscarred). Tubular epithelial nuclei are considered positive (viral replication) with the typical viral inclusions and/or positive immunohistology (usually SV-40 large T antigen). Note that pvl is not determined by the ratio of positive nuclei to all nuclei but by the ratio of tubules/ducts with at least one positive nucleus to all tubules/ducts. Banff Lesion Scores pvl and ci yield the Class of Polyomavirus Nephropathy 1 (pvl1 and ci≤1), 2 (all other combinations of pvl and ci not qualifying for class 1 or 3) or 3 (pvl3 and ci≥2).25 Polyomavirus Nephropathy is formally recognized among the Category 6 diagnoses.
pvl0 – no positive nuclei in any tubules/ducts pvl1 – ≤1% of all tubules/ducts
pvl2 – >1% to ≤10% of all tubules/ducts
pvl3 – >10% of all tubules/ducts
Table 1
Table 1: This is a synopsis of the thresholds for all Banff Lesion Scores. The user of this table should be familiar with the exact definitions underlying each individual Banff Lesion Score. Reliance on these thresholds alone without consideration of the regulatory statutes behind these scores is strongly discouraged. Abbreviations: EM: electron microscopy, LM: light microscopy, max: maximum, PTC: peritubular capillary
| Banff lesion score, | Abbreviation | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interstitial inflammation | i | <10% | 10-25% | 26-50% | >50% |
| Tubulitis | t | None | 1-4/tubular cross section or 10 tubular epithelial cells | 5-10 | >10 OR (foci of tubular basement membrane destruction with i ≥ 2 and t2 elsewhere) |
| Intimal arteritis | v | None | <25% luminal area lost | ≥25% luminal area lost | Transmural and/or fibrinoid change and medial smooth muscle necrosis |
| Glomerulitis | g | None | <25% | 25-75% | >75% |
| Peritubular capillaritis | ptc | <3 leukocytes/PTC | ≥1 leukocyte in ≥10% of PTCs with max. of 3-4/PTC | ≥1 leukocyte in ≥10% of PTCs with max. of 5-10/PTC | ≥1 leukocyte in ≥10% of PTCs with max. of >10/PTC |
| C4d | C4d | None | <10% | 10-50% | >50% |
| Interstitial fibrosis | ci | ≤5% | 6-25% | 26-50% | >50% |
| Tubular atrophy | ct | None | ≤25% | 26-50% | >50% |
| Vascular fibrous Intimal thickening | cv | None | ≤25% | 26-50% | >50% reduction in luminal area |
| GBM double contours | cg | None | 1a: only by EM 1b: ≤25% by LM | 26-50% | >50% of the most affected nonischemic, nonsclerotic glomerulus |
| Mesangial matrix expansion | mm | None | ≤25% | 26-50% | >50% of nonsclerotic glomeruli |
| Arteriolar hyalinosis | ah | None | Mild to moderate in ≥1 | Moderate to severe in >1 | Severe in many |
| Hyaline arteriolar thickening | aah | None | 1 without circumferentia | ≥1 without circumferentia | circumferential |
| Total inflammation | ti | <10% | 10-25% | 26-50% | >50% |
| Inflammation in the area of IFTA | i-IFTA | <10% | 10-25% | 26-50% | >50% |
| Tubulitis in areas of interstitial fibrosis | t-IFTA | None | 1-4/tubular cross section or 10 tubular epithelial cells | 5-10 | >10 |
| Polyomavirus Load | pvl | ≤1% | >1% | ≤10% | >10% |
Table 2
Table 2: These Additional Diagnostic Parameters, some histopathologic, some clinical, some molecular, are derived from the diagnostic algorithms in Table 1. Depending on the constellation of findings in each individual case, and access to molecular diagnosis, these Additional Diagnostic Paramenters may be used in addition to the Banff Lesion Scores to determine the Banff Diagnostic Categories.
| Parameters | Required for diagnostic category |
|---|---|
| Acute Thrombotic Microangiopathy In The Absence Of Any Other Cause (Figure 19) | Active and Chronic Active AMR |
| Absence Of Recurrent Or De Novo Glomerulonephritis | Active and Chronic Active AMR |
| Infection | Active and Chronic Active AMR |
| Biopsy-based transcript diagnostics for AMR/MVI above a defined threshold, if thoroughly validated for use as a substitute for AMR/MVI and available | Active AMR, Chronic Active AMR, Chronic AMR |
| Severe Peritubular Capillary Basement Membrane Multilayering (Figure 19) | Chronic AMR and Chronic Active AMR |
| Arterial Intimal Fibrosis With Mononuclear Cell Inflammation In Fibrosis And Formation Of Neointima | Chronic Active TCMR Grade II |
| Prior Evidence Of DSA | Chronic AMR |
| Serologic Evidence Of DSAs (DSA To HLA Or Other Antigens) | Active AMR, Chronic Active AMR |
| Prior Documented Diagnosis Of Active Or Chronic Active AMR | Chronic AMR |
| Evidence Of Chronic TMA | Chronic Active AMR and Chronic AMR |
| C4d Staining On Fresh-Frozen Or Paraffin-Embedded Tissue | C4d Staining Without Evidence Of Rejection, Active AMR, Chronic Active AMR, Chronic AMR |
| Polyomavirus Nephropathy, Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder, Calcineurin Inhibitor Toxicity, Acute Tubular Injury Recurrent Disease, De Novo Glomerulopathy (Other Than TG), Pyelonephritis, Drug-Induced Interstitial Nephritis | Other Changes Not Considered To Be Caused By Acute Or Chronic Rejection |
| Other Known Causes Of i-IFTA Ruled Out | Chronic Active TCMR IA and IB |
| Acute Tubular Injury | C4d staining with acute tubular injury |
Illustrations for PTCML and TMA

Figure 18. Banff Additional Diagnostic Parameter ptcml (peritubular capillary basement membrane multilayering) is only demonstrable by EM. A, This Additional Diagnostic Parameter is a criterion for AMR chronicity. It is defined as 7 or more layers of basement membrane in at least a single cortical peritubular capillary and 5 or more in at least 2 additional capillaries. This particular capillary shows 8 layers (arrow). Transmission EM, original magnification x14,000. B, this image demonstrates a peritubular capillary with 5 layers of basement membrane (arrow). Transmission EM, original magnification x10,000.
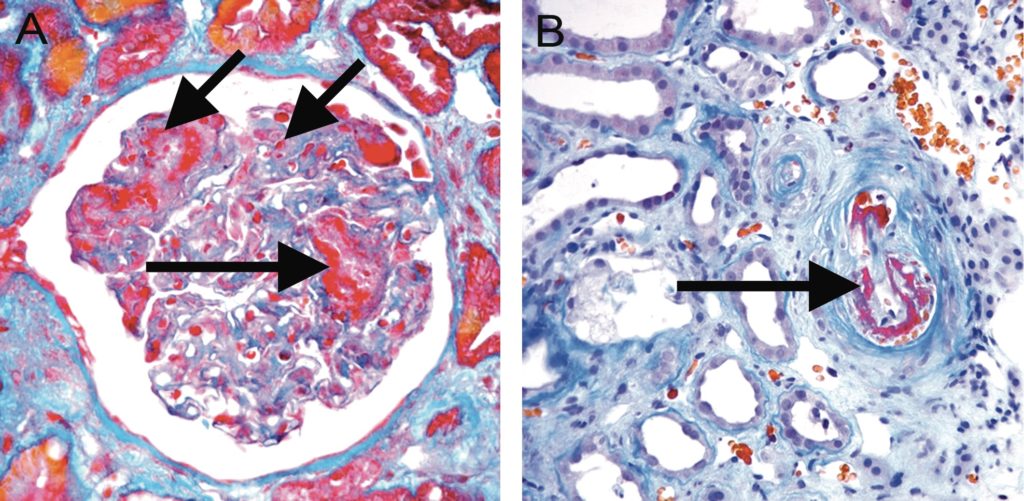
Figure 19. Acute TMA. A, Acute TMA affecting a glomerulus with fibrin thrombi (long arrows) and fragmented red blood cells (short arrow) in capillary loops. Trichrome, original magnification x400. B, Acute TMA affecting a small arteriole (arrow). Acute TMA is one of the histological features used as histological evidence of acute tissue injury in Active AMR. However, TMA is not specific for AMR and can be seen in, for example, recurrent disease or calcineurin inhibitor toxicity. Trichrome, original magnification x400.
BANFF DIAGNOSTIC CATEGORIES
Table 3 presents the Banff Diagnostic Categories and is based on a table in the Banff update from 2017,12 incorporating changes from 2019 and 2022.13-14 Banff consensus supports giving both a diagnosis of Borderline (Cat. 3) or Acute TCMR alongside a diagnosis of Chronic Active TCMR, if both are present.13 Banff 2022 introduces a flow-chart, reasoning framework and clinical interpretation figure and tables, to help with implementation of Category 2. These are included below Table 3. Readers should stay alert to future updates on the Banff Foundation website (www.banfffoundation. org) informed by updates to the Banff Classification from 2024 onward.
Table 3
| Table 3: Banff Diagnostic Categories form the core of the Banff Classification of Renal Transplant Pathology. We refer to the Banff Lesion Scores in the main body of this review as well as to the Additional Diagnostic Parameters listed in Table 2. Note that diagnoses from various Banff Diagnostic Categories can coexist in a given biopsy, e.g. Acute TCMR Grade IB, Chronic Active ABMR, moderate Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy and Calcineurin Inhibitor Toxicity. From each Banff Diagnostic Category except for 6, only one diagnosis must be made. Banff also suggests that giving both Borderline (Cat. 3) and Acute TCMR diagnoses together with Chronic Active TCMR diagnoses from Cat. 4 could improve reporting. For Category 2, note that other lesions can be observed in AMR that strengthen the diagnosis but are not diagnostic on their own as isolated features: acute tubular injury, in the absence of any other apparent cause (active AMR), arterial intimal fibrosis (cv) of new onset, excluding other causes (chronic active and chronic AMR); leukocytes within the sclerotic intima favour chronic active or chronic AMR if there is no prior history of TCMR. |
| CATEGORY 1: Normal Biopsy Or Nonspecific Changes Requires exclusion of any diagnosis from the Banff Diagnostic Categories 2-4, 6 below. | ||
| CATEGORY 2: Antibody-mediated rejection and microvascular inflammation/injury (AMR/MVI) | ||
| Active AMR; All 3 criteria must be met for diagnosis | ||
*Can be observed in AMR and strengthen the diagnosis but not diagnostic in itself: acute tubular injury, in the absence of any other apparent cause |
||
| Chronic active AMR; all 3 criteria must be met for diagnosis | ||
*Other lesions can be observed in AMR and strengthen the diagnosis but are not diagnostic by themselves: arterial intimal fibrosis (cv) of new onset, excluding other causes; leukocytes within the sclerotic intima favour chronic AMR if there is no prior history of TCMR; |
||
| Chronic AMR; all 3 criteria must be met for diagnosis | ||
| 1. cg > 0 and/or severe ptcml 2. Absence of criterion 2 as defined for active and chronic active AMR, above 3. Prior documented diagnosis of active or chronic active ABMR and/or documented prior (post-transplant) and/or current evidence of DSA (DSA as defined in above criterion 3 for active AMR) |
||
| C4d staining without evidence of rejection; all 4 features must be met for diagnosisc | ||
| 1. Linear C4d staining in peritubular capillaries (C4d2 or C4d3 by IF on frozen sections, or C4d > 0 by IHC on paraffin sections) 2. Criterion 1 for active or chronic active AMR not met 3. Negative biopsy-based transcript diagnostics for AMR/MVI as in criterion 2 for active and chronic active AMR 4. No acute or chronic active TCMR, or borderline changes |
||
| Microvascular inflammation/injury (MVI), DSA-negative and C4d-negative; all 3 criteria must be met for diagnosis | ||
| 1. At least moderate microvascular inflammation ([g + ptc] ≥2) in the absence of recurrent or de novo glomerulonephritis, although in the presence of acute TCMR, borderline infiltrate, or infection, ptc ≥ 2 alone is not sufficient and g must be ≥1 2. No linear C4d staining in peritubular capillaries (C4d0 or C4d1 by IF on frozen sections, or C4d = 0 by IHC on paraffin sections) 3. No serologic evidence of circulating donor-specific antibodies (DSA to HLA or other antigens, as defined in above criterion 3 for active AMR) |
||
| Probable AMR; all 4 criteria must be met for diagnosis | ||
| 1. Identical to criterion 1 for active AMR, above 2. Criterion 1 for chronic active and chronic AMR not met 3. Absence of criterion 2 defined for active and chronic active AMR, above 4. Identical to criterion 3 for active AMR, above (but C4d must be negative) |
||
| C4d staining with acute tubular injury (ATI); all 3 criteria must be met for diagnosis | ||
Clinical scenarios:
|
||
|
CATEGORY 3: Suspicious (Borderline) For Acute TCMR
Foci of Banff Lesion Score t>0 AND Banff Lesions Score i=1 OR Foci of Banff Lesion Score t1 AND Banff Lesion Score i ≥ 2 |
||
|
CATEGORY 4: TCMR
Acute TCMR IA Banff Lesion Score i ≥ 2 AND Banff Lesion Score t2 Acute TCMR IB Banff Lesion Score i ≥ 2 AND Banff Lesion Score t3 Acute TCMR IIA Banff Lesion Score v1 regardless of Banff Lesion Scores i or t Acute TCMR IIB Banff Lesion Score v2 regardless of Banff Lesion Scores i or t Acute TCMR III Banff Lesion Score v3 regardless of Banff Lesion Scores i or t Chronic Active TCMR Grade IA Banff Lesion Score ti ≥ 2 AND Banff Lesion Score i-IFTA ≥ 2, other known causes of i-IFTA (eg, pyelonephritis, BK-virus nephritis etc.) ruled out AND Banff Lesion Score t2 Chronic Active TCMR Grade IB Banff Lesion Score ti ≥ 2 AND Banff Lesion Score i-IFTA ≥ 2, other known causes of i-IFTA ruled out AND Banff Lesion Score t3 Chronic Active TCMR Grade II Arterial intimal fibrosis with mononuclear cell inflammation in fibrosis and formation of neointima |
||
| CATEGORY 5: IFTA | ||
|
Grade I (Mild) Banff Lesion Score ci1 OR Banff Lesion Score ct1
Grade Il (Moderate) Banff Lesion Score ci2 OR Banff Lesion Score ct2 Grade III (Severe) Banff Lesion Score ci3 OR Banff Lesion Score ct3 |
||
| CATEGORY 6: Other Changes Not Considered To Be Caused By Acute Or Chronic Rejection (Figure 20) | ||
| Polyomavirus Nephropathy, Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder, Calcineurin Inhibitor Toxicity, Acute Tubular Injury, Recurrent Disease, De Novo Glomerulopathy (Other Than TG), Pyelonephritis, Drug-Induced Interstitial Nephritis | ||
Flowchart of the Banff 2022 Classification for Category 2: Antibody-mediated rejection and microvascular inflammation/injury (AMR/MVI).
This can be used as companion for disease classification but does not modify the detailed Banff Classification for Category 2 AMR/MVI.
a. Other lesions can be observed in AMR and strengthen the diagnosis but are not diagnostic by themselves: arterial intimal fibrosis (cv) of new onset, excluding other causes; leukocytes within the sclerotic intima favour chronic AMR if there is no prior history of TCMR; acute tubular injury, in the absence of any other apparent cause.
b. Definitions of “diagnostic features of AMR/MVI”: g>0 in the absence of glomerulonephritis; ptc > 0 in the absence of acute TCMR or borderline (suspicious) for acute TCMR; v>0; acute thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) in the absence of any other cause; cg>0 by LM, or EM if available, if no evidence of chronic TMA and if absence of recurrent or de novo glomerulonephritis; ptcml = seven or more layers in 1 cortical peritubular capillary and 5 or more layers in 2 additional capillaries, avoiding portions cut tangentially by EM, if available.
c. [g + ptc ≥ 2] in the absence of recurrent or de novo glomerulonephritis. If borderline (suspicious) for or acute TCMR, or infection are present, [g + ptc ≥ 2] is not sufficient and Banff lesion score g≥1 is required.
d. Biopsy-based transcript diagnostics for AMR/MVI above a defined threshold, if thoroughly validated for use a substitute for AMR/MVI and available.
e. In cases of MVI below threshold, biopsy-based transcript diagnostics can be applied, if thoroughly validated for use as a substitute for AMR/MVI and available.
f. C4d deposition should be evaluated in peritubular capillaries and vasa recta (C4d positive = C4d2 or C4d3 by IF on frozen sections, C4d >0 by IHC on paraffin sections).
g. If thorough testing for DSA (anti-HLA or other specificity) has not yet been performed, this should be done, following the STAR guidelines. Detection of non-HLA antibodies (including ABO antibodies in ABO-incompatible transplantation) can be used as serologic Banff criterion for diagnosis of AMR, if the testing protocols are sufficiently standardized and clinically validated for the appropriate clinical context. At present, no non-HLA antibodies (apart from ABO antibodies) have been validated sufficiently for inclusion into the routine clinical classification of kidney transplant biopsies.
h. Upon diagnosis of AMR, further differentiation of disease stage is as follows. Active AMR: presence of only active features (including C4d positivity) (cg=0; ptcml=0); Chronic active AMR: presence of both active (including C4d positivity) and chronic (cg>0 and/or severe ptcml) features.
i Cases with “Probable AMR” and histological chronic lesions (cg or ptcml) can be labelled as “chronic AMR”. For these cases, prior documented diagnosis of active or chronic active AMR, or documented prior evidence of DSA, also count as DSA positivity.
Reasoning framework for Banff 2022 Category 2: Antibody-mediated rejection and microvascular inflammation/injury (AMR/MVI)
This can be used as companion for disease classification alongside the flowchart, but does not modify the detailed Banff Classification for Category 2 AMR/MVI.
Clinical interpretation of Banff Category 2: Antibody-mediated rejection and microvascular inflammation/injury (AMR/MVI)
The text in this Table can be used in the Comments section of a transplant renal biopsy pathology report, to support standardised communication between pathologists and clinicians around the meaning of the terminology of diseases covered in Category 2.
| Clinical interpretation of Banff Category 2: Antibody-mediated rejection and microvascular inflammation/injury (AMR/MVI) | |
| Antibody-mediated (AMR) | AMR can be diagnosed in patients with normal or abnormal kidney function. Further differentiation into active AMR, chronic active AMR, and chronic AMR, can guide therapeutic decision-making. |
|
Probable AMR
|
In the context of circulating DSA, individual lesions of MVI (g, ptc, v, acute TMA, cg, ptcml) below the histological threshold for MVI (g+ptc<2) and in the absence of C4d deposition in peritubular capillaries, probably indicate antibody activity. This phenotype can be diagnosed in patients with normal or abnormal kidney function. Depending on the clinical context, antibody-targeted treatment could be considered. Further research is necessary to determine the prevalence, impact, and best treatment for this phenotype. |
| MVI, DSA-negative and C4d-negative | MVI above the histological threshold, without circulating DSA and with negative C4d staining in peritubular capillaries has been observed in patients with normal or abnormal kidney function. This is a purely descriptive phenotype, and the cause remains unclear. Before assigning cases as DSA negative, thorough evaluation of all loci and interactions with the HLA laboratory is necessary, following the STAR guidelines, and the limitations of DSA testing should be considered. Further research is necessary to determine the prevalence, the causes and related biological processes and best treatment for this pattern. These cases may represent missed HLA-DSA, alloreactive T cell mediated responses; autoreactive or alloreactive non-HLA antibodies; primary NK cell activation through missing self; viral infection; other mechanisms of innate immune activation; ischemia reperfusion injury, etc. |
CRITICAL APPRAISAL
Since 1991, the Banff classification has undergone several amendments, reflecting the growing body of knowledge in transplant pathology. These amendments have been based on a consensus reached at the biannual Banff meetings. This constant refinement based on emerging data is a strength of the Banff process and has led to the worldwide dominance of the Banff Classification for diagnostic practice, research and clinical trials. However, the iterative fashion in which the definitions and rules were published has dispersed the relevant content and created ambiguities. This has led to the creation of the Banff Rules and Dissemination Working Group in the aftermath of the Banff Meeting in Barcelona in March 2017. The aim of the Working group is not to alter the content of the Banff Classification. Rather, it shall collate all relevant Banff content in a central repository under the auspices of the Banff Foundation for Transplant Pathology, with a single updatable content, similar to the Union for International Cancer Control’s TNM Classification. Changes in the content of the Banff Classification must only be made through review of evidence and expert consensus at the Banff meetings or within the relevant other Working Groups. Like the collation of content above, the following critical appraisal is based on this mission and does not touch on the content of the Banff Classification itself. Although the Banff Lesion Scores required for a diagnosis of AMR have undergone a partial overhaul10 and although a dedicated Working Group is reexamining the Banff Lesion Scores for TCMR, no or little effort has been devoted to the Additional Diagnostic Parameters in Table 2. The Banff 2022 meeting partly addressed this by obtaining consensus for the removal from the definition of AMR of poorly defined and/or largely redundant features such as “Acute Tubular Injury In The Absence Of Any Other Cause” as a criterion for active AMR. Another example is “Infection,” which precludes the use of Banff Lesion Score ptc alone as a criterion for AMR.12 Use of the isolated term “infection” is ambiguous in the context of whether inflammation in the transplant should be considered as evidence for rejection or not. We would recommend treating these Additional Diagnostic Parameters like the Banff Lesion Scores, presenting them in clear and consistent wording, and, whenever necessary, by providing guidance through meaningful definitions elaborated over time through Working Groups and in alignment with the respective diagnostic criteria applied.
Among the Banff Lesion Scores, the Banff Lesion Score cv has a confusing array of terminologies, appearances and diagnostic implications. “Arterial fibrointimal thickening” or “vascular fibrous intimal thickening” imply a chronic fibrous change, whereas arterial intimal thickening can be cellular and nonfibrous in “transplant vasculopathy” or “chronic allograft arteriopathy”. As a manifestation of chronic TCMR, it is defined as “arterial intimal fibrosis with mononuclear cell infiltration in fibrosis, and formation of neointima”.12 There is also evidence in both animal models and in humans that anti-HLA antibodies can induce accelerated atherosclerosis in large and medium arteries, and that this can have a detrimental effect on transplant function. However, the practical use of this histologic feature is problematic, and the Banff 2022 Survey reached consensus that “arterial intimal fibrosis of new onset” should not be used for the diagnosis of AMR when present on its own, without other key histological features of AMR. Although there is no question about its scientific validity as a feature of antibody-mediated injury, the clinical usefulness of this feature is limited for several reasons: arterial intimal fibrosis is highly prevalent, arterial sampling in biopsies is generally low, reproducibility of the scoring of degree of arterial fibrosis is lower than other features, and also because this feature requires a previous biopsy, which is not available in many cases. After the Banff 2022 Survey, this non-specific lesion was eliminated from the key diagnostic definitions, on their own sufficient for diagnosis of AMR. Nevertheless, it is recommended to report on “arterial intimal fibrosis of new onset” and comment on its known association with anti-HLA antibodies in clinical routine, as the presence of this feature further reinforces a diagnosis of (Probable) AMR if the strict diagnostic definitions are met. “New onset” (requiring earlier biopsy) of arterial intimal fibrosis is not the only relevant arterial feature. Lack of fibroelastosis is considered more suggestive of AMR, even though after the first months post-transplant, fibroelastosis can also develop in AMR, limiting diagnostic usefulness. Hypercellularity of the fibrotic/thickened intima is also considered as more specific of ongoing AMR but is not clearly defined and is also a diagnostic feature of chronic active TCMR.
A related problem is attached to Banff Lesion Score cg: “evidence of chronic thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA)” excludes the use of Banff Lesion Score cg > 0 as a criterion for AMR chronicity, whereas Active AMR can be diagnosed with TMA, as long as it is “in the absence of any other cause [than AMR]”. Because Active AMR causing TMA can lead to glomerular lesion qualifying as TG, it would make sense to change the cg criterion to only exclude chronic TMA of any other cause than AMR. The use of asterisks (“*”) attached to Banff Lesion Scores v, i, ah and ptc5,7is problematic and widely neglected. Their reproducibility and diagnostic value are unknown, and they are ambiguous: an asterisk behind the Banff Lesion Score ptc signifies only mononuclear cells and absence of neutrophils, whereas the asterisk behind Banff Lesion Score i denotes a significant neutrophilic, eosinophilic or plasmacellular component in the infiltrate, and these different cell types can have widely differing implications. We suggest the Banff community should reassess these modifiers, either by improving their definitions and assigning them a significance or by abandoning them. Inevitably, the Banff Classification has focused mainly on features of rejection, but with Banff Lesion Scores developed for other features with little or no guidance on their contribution to diagnosis. An example for this is Banff Lesion Score aah, originally intended to replace the poorly reproducible Banff lesion score ah.7 However, its use is still optional, and it has neither been widely adopted nor used in any of the Banff Diagnostic Categories. The Banff community should reassess arteriolar hyalinosis lesion scores, and clarify grading and diagnostic implications. Regarding the Banff Diagnostic Categories, a clear diagnostic pathway should be recommended when dealing with Borderline or Acute TCMR (Banff Diagnostic Categories 3 and 4) in the presence of Polyomavirus Nephropathy, Pyelonephritis or other infectious diseases of the transplant, as well as AMR with glomerulitis in the presence of recurrent or de novo glomerulonephritis. These issues could be referred to the Banff TCMR and Glomerulonephritis Working Group respectively. There are uncertainties around the application of transmission EM in the diagnosis of AMR which are currently being addressed by the Electron Microscopy Working Group. These issues include precise guidelines for indications and methods for application of EM in transplant biopsies; perhaps also the introduction of a new Banff Lesion Score for multilamination of the basement membranes of peritubular capillaries which we have covered as an Additional Diagnostic Parameter for now. Another critical issue is related to the molecular diagnostics of AMR and TCMR. Although the current Banff classification endorses the use of molecular diagnostics in the definition of AMR, there is limited guidance regarding methods and diagnostic cut-offs, which could be elaborated by the Molecular Working Group. Lastly, the introduction of the new diagnostic categories of Chronic Active TCMR is likely to undergo changes informed by the TCMR Working Group. Before Banff 2017, there were no specific criteria for Chronic Active TCMR outside of arteries, and tubulitis was only scored in non-atrophic and mildly atrophic tubules, effectively excluding moderately and severely atrophic tubules. To avoid having two separate criteria for Banff Lesion Score t in Acute versus Chronic Active TCMR, it was decided that for both diagnoses tubulitis would be scored in all tubules except severely atrophic tubules. The difference between Banff 2017 and previous versions of the classification with respect to Acute TCMR is that tubulitis in moderately atrophic tubules is now counted toward Banff Lesion Score t in cortical areas without interstitial fibrosis, whereas t-IFTA is counted in cortical areas with interstitial fibrosis. Because the latter was done for clarity and to avoid confusion rather than on the basis of specific evidence, it would be beneficial that future studies be done to address the most clinically relevant threshold for the level of atrophy permitted in scoreable tubules, especially for diagnosis of Acute TCMR. In addition, the 2017 changes to the TCMR criteria also suggest future work be aimed at examining the response of Chronic Active TCMR to steroids and other anti–T cell therapies (e.g. thymoglobulin), determining if there are differences in this response between: (1) Grade IA versus Grade IB Chronic Active TCMR and (2) biopsies with Chronic Active TCMR that would otherwise meet criteria for acute TCMR (i.e. with Banff Lesion Score i ≥ 2) and those that would not (with Banff Lesion Score i ≤ 1).
PROSPECTS
Going forward, this web resource will serve as the continuously updated go-to resource for the relevant Banff content, with the regular Banff update manuscripts providing the detailed reasoning for changes. Depending on the progress in the definitions and diagnostic rule sets we are aiming to develop web-based resources such as diagnostic algorithms to further strengthen standardization and reproducibility of the Banff Classification for clinical practice and research. It should be emphasized that the Banff Classification of Kidney Transplant Pathology does not cover all relevant aspects of transplantation medicine. Allograft transplantation only reaches 10% of patients needing new organs. Through regenerative medicine and tissue engineering and other optimizing initiatives we will eventually be able to provide organs to everyone in need. For this, we will need a new Banff Classification of Tissue Engineering Pathology26,27 reflecting the new challenges of delivering the right cells to the right places in a bioengineered organ and having them function normally. Rejection will no longer be the primary threat in bioengineered organs. For a decade or more the new Banff Classification of Tissue Engineering Pathology will be used concurrently with the existing Banff Classification of Transplant Pathology. Getting the right cells in the right places sounds simple, but in fact, we have poor knowledge of what all the normal cell types in transplanted organs are. For instance, in the kidney, we have traditionally taught that there are 26 cell types,28 but in fact, high throughput single cell analysis in the Human Cell Atlas Project shows many more than that and can determine not only cell identity but also lineage and activation state.29-32 The transplantation and transplantation pathology community needs to embrace Human Cell Atlas technology, so we are not blindsided by this new technology. The scale of the likely impact of the Human Cell Atlas Project on nephrology and transplantation is currently being analyzed.33
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge the help in the preparation of the visual analog scales from Christopher Bellamy, Alton “Brad” Farris and Daniel Serón as well as the web design by Devansh Bhatt and Celina Schulz.
REFERENCES
1 Solez, K. et al. International standardization of criteria for the histologic diagnosis of renal allograft rejection: the Banff working classification of kidney transplant pathology. Kidney international 44, 411-422 (1993).
2 Gouldesbrough, D. R. & Axelsen, R. A. Arterial endothelialitis in chronic renal allograft rejection: a histopathological and immunocytochemical study. Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation : official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association – European Renal Association 9, 35-40 (1994).
3 Becker, J. U., Chang, A., Nickeleit, V., Randhawa, P. & Roufosse, C. Banff borderline changes suspicious for acute T-cell mediated rejection: where do we stand? American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons, doi:10.1111/ajt.13784 (2016).
4 Solez, K. et al. Report of the Third Banff Conference on Allograft Pathology (July 20-24, 1995) on classification and lesion scoring in renal allograft pathology. Transplantation proceedings 28, 441-444 (1996).
5 Racusen, L. C. et al. The Banff 97 working classification of renal allograft pathology. Kidney international 55, 713-723 (1999).
6 Racusen, L. C., Halloran, P. F. & Solez, K. Banff 2003 meeting report: new diagnostic insights and standards. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 4, 1562-1566 (2004).
7 Solez, K. et al. Banff ’05 Meeting Report: differential diagnosis of chronic allograft injury and elimination of chronic allograft nephropathy (‘CAN’). American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 7, 518-526, doi:AJT1688 [pii] 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2006.01688.x (2007).
8 Solez, K. et al. Banff 07 classification of renal allograft pathology: updates and future directions. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 8, 753-760, doi:AJT2159 [pii] 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02159.x (2008).
9 Mengel, M. et al. Banff 2011 Meeting Report: New Concepts in Antibody-Mediated Rejection. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 12, 563-570, doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03926.x (2012).
10 Haas, M. et al. Banff 2013 meeting report: inclusion of c4d-negative antibody-mediated rejection and antibody-associated arterial lesions. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 14, 272-283, doi:10.1111/ajt.12590 (2014).
11 Loupy, A. et al. The Banff 2015 Kidney meeting report: Current challenges in rejection classification and prospects for adopting molecular pathology. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 17, 28-41, doi:10.1111/ajt.14107 (2017).
12 Haas, M. et al. The Banff 2017 Kidney Meeting Report: Revised Diagnostic Criteria for Chronic Active T Cell-Mediated Rejection, Antibody-Mediated Rejection, and Prospects for Integrative Endpoints for Next-Generation Clinical Trials. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons, doi:10.1111/ajt.14625 (2017).
13 Loupy, A. et al. The Banff 2019 Kidney Meeting Report (I): Updates on and clarification of criteria for T cell- and antibody-mediated rejection. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons, doi:10.1111/ajt.15898 (2020).
14 Naesens, M. Roufosse C. et al. The Banff 2022 Kidney Meeting Report: Reappraisal of microvascular inflammation and the role of biopsy-based transcript diagnostics. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons, doi:10.1016/j/ajt (2023).
15 Tambur AR, Campbell P, Claas FH, et al. Sensitization in Transplantation: Assessment of Risk (STAR) 2017 Working Group Meeting Report. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons, doi:10.1111/ajt.14752 (2018).
16 Tambur AR, Campbell P, Chong AS, et al. Sensitization in transplantation: Assessment of risk (STAR) 2019 Working Group Meeting Report. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons, DOI:10.1111/ajt.15937 (2020).
17 Lefaucheur C, Louis K, Morris AB, et al. Clinical recommendations for posttransplant assessment of anti-HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigen) donor-specific antibodies: A Sensitization in Transplantation: Assessment of Risk consensus document. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons, DOI: 10.1016/j.ajt.2022.11.013 (2023).
18 Liapis, H. et al. Banff Histopathological Consensus Criteria for Preimplantation Kidney Biopsies. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 17, 140-150, doi:10.1111/ajt.13929 (2017).
19 Ishii, Y. et al. Loss of peritubular capillaries in the development of chronic allograft nephropathy. Transplantation proceedings 37, 981-983, doi:S0041-1345(04)01742-7 [pii] 10.1016/j.transproceed.2004.12.284 [doi] (2005).
20 Farris, A. B. et al. Banff fibrosis study: multicenter visual assessment and computerized analysis of interstitial fibrosis in kidney biopsies. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 14, 897-907, doi:10.1111/ajt.12641 (2014).
21 Mengel, M. et al. Scoring total inflammation is superior to the current Banff inflammation score in predicting outcome and the degree of molecular disturbance in renal allografts. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 9, 1859-1867, doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.02727.x (2009).
22 Mannon, R. B. et al. Inflammation in areas of tubular atrophy in kidney allograft biopsies: a potent predictor of allograft failure. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 10, 2066-2073, doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03240.x (2010).
23 Lefaucheur, C. et al. T cell-mediated rejection is a major determinant of inflammation in scarred areas in kidney allografts. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 18, 377-390, doi:10.1111/ajt.14565 (2018).
24 Nankivell, B. J. et al. The causes, significance and consequences of inflammatory fibrosis in kidney transplantation: The Banff i-IFTA lesion. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 18, 364-376, doi:10.1111/ajt.14609 (2018).
25 Nickeleit, V. et al. The Banff Working Group Classification of Definitive Polyomavirus Nephropathy: Morphologic Definitions and Clinical Correlations. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN 29, 680-693, doi:10.1681/ASN.2017050477 (2018).
26 Roufosse, C. et al. A 2018 Reference Guide to the Banff Classification of Renal Allograft Pathology. Transplantation, doi:10.1097/TP.0000000000002366 (2018).
27 Solez, K. et al. The bridge between transplantation and regenerative medicine: Beginning a new Banff classification of tissue engineering pathology. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons, doi:10.1111/ajt.14610 (2017).
28 Solez, K. Kim Solez, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada Banff: A Unique Start Setting Standards for Consensus Conferences. Transplantation 101, 2264-2266, doi:10.1097/TP.0000000000001901 (2017).
29 Al-Awqati, Q. & Oliver, J. A. Stem cells in the kidney. Kidney international 61, 387-395, doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00164.x (2002).
30 Regev, A. et al. The Human Cell Atlas. Elife 6, doi:10.7554/eLife.27041 (2017).
31 Stubbington, M. J. T., Rozenblatt-Rosen, O., Regev, A. & Teichmann, S. A. Single-cell transcriptomics to explore the immune system in health and disease. Science 358, 58-63, doi:10.1126/science.aan6828 (2017).
32 Rozenblatt-Rosen, O., Stubbington, M. J. T., Regev, A. & Teichmann, S. A. The Human Cell Atlas: from vision to reality. Nature 550, 451-453, doi:10.1038/550451a (2017).
33 Moghe, I., Loupy, A. & Solez, K. The Human Cell Atlas Project by the numbers: Relationship to the Banff Classification. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 18, 1830, doi:10.1111/ajt.14757 (2018).
34 Regele, H. et al. Capillary deposition of complement split product C4d in renal allografts is associated with basement membrane injury in peritubular and glomerular capillaries: a contribution of humoral immunity to chronic allograft rejection. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN 13, 2371-2380 (2002).
35 Bonsib, S. M. in Heptinstall’s Pathology of the Kidney Vol. 1 (eds C. J. Jennette, F. G. Silva, J. L. Olson, & V. D. D’Agati) Ch. 1, 1-66 (Lippincot Williams & Wilkins, 2015).
36 Noris, M. & Remuzzi, G. Thrombotic microangiopathy after kidney transplantation. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 10, 1517-1523, doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03156.x (2010).
37 Hill, G. S. et al. Donor-specific antibodies accelerate arteriosclerosis after kidney transplantation. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN 22, 975-983, doi:10.1681/ASN.2010070777 (2011).
Glossary of Terms
Acute Tubular Injury
There is no current definition of acute tubular injury endorsed by the Banff classification. Acute Tubular Injury without other specification is included as a diagnosis in Banff Diagnostic Category 6.
Antibody Mediated Rejection (AMR)
Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) refers to a rejection process believed to be primarily driven by antibodies against graft epitopes. Diagnostic criteria are listed under Banff Diagnostic Category 2 of the 2017 Banff update.12 Diagnostic subcategories within include the following; C4d Staining Without Evidence of Rejection, Active AMR, Chronic Active AMR, Chronic AMR. AMR can coexist with additional diagnoses from Banff Diagnostic Categories 3-6.
Adequacy of Specimen
Since Banff 1997 a biopsy has been considered adequate if it contains at least 10 or more glomeruli and at least 2 arteries; the threshold for a “minimal sample” is 7 glomeruli and 1 artery.5 It is also recommended that at least 2 separate cores containing cortex be obtained or that there be 2 separate areas of cortex in the same core.11 In the recent consensus manuscript on polyomavirus nephropathy for the determination of Banff Score pvl adequacy requires medulla in the biopsy in addition to the two cores.22
Arteriole
Derived from the definition of arteries below, the definition of arterioles is consequently arterial vessels having less than two smooth muscle layers.11Changes in arterioles are currently not recognised as contributory to Banff Lesion Score v or cv.12 Arteriolar inflammation is noted with an asterisk behind Banff Lesion Score ah, e.g. ah2*.5
Arteritis, Intimal
Arteritis is synonymous with endarteritis or arterial endothelialitis. According to Banff 2015, intimal arteritis as per Banff Lesion Score v1, v2 is defined as mononuclear cell infiltration beneath the arterial endothelium. Severe arteritis v3 is defined by inflammation in the media and/or fibrinoid necrosis of the vessel wall; the total number of arteries in the biopsy and the number of arteries affected should be noted.11 Marginated leukocytes alone are insufficient to diagnose arteritis.
Artery
Since Banff 20134 an artery has been defined by “having a continuous media with two or more smooth muscle layers”.11
Banff Diagnostic Categories
This refers to the six consensus-based and empirically validated Banff Diagnostic Categories (1 to 6) for renal allograft biopsies.12 Any diagnosis from Categories 2-6 excludes Banff Diagnostic Category 1 (Normal Biopsy or Nonspecific changes). Multiple diagnoses from a single Banff Diagnostic Category can only be made from Category 4 and 6.
Banff Lesion Scores
Banff Lesion Scores are descriptive, consensus-based, standardised terms to grade important active and chronic histopathological findings in the different morphological compartments of the renal transplant. Although they are an integral part of the minimal dataset, they are by themselves not necessarily sufficient to determine Banff Diagnostic Categories.
Biopsy-based transcript diagnostics for AMR/MVI above a defined threshold, if thoroughly validated for use a substitute for AMR/MVI and available.
Increased expression of these, if thoroughly validated, is the only molecular marker considered in the Banff classification. Since Banff 201310 they have been included in Banff Diagnostic Category 2 for the diagnosis of Active AMR and Chronic Active AMR.11
Borderline Changes
This refers to Banff Diagnostic Category 3 “Suspicious (Borderline) for Acute TCMR”.12 This can be used in conjunction with other Banff categories with the exception of Category 1 (Normal Biopsy Or Nonspecific Changes).
C4d
Complement component 4 fragment d (C4d) is a degradation product of complement component C4, which can bind covalently to the endothelial cell surface.34 Positive immunostaining indicates local complement activation and is scored with Banff Lesion Score C4d.11 The clinical significance of these findings is different in grafts exposed to anti-blood group antibodies (ABO-incompatible allografts), in which isoagglutinin-mediated complement activation does not appear to be injurious to the graft and may represent accommodation. However, when caused by donor-specific antibodies against HLA or other antigens, it may indicate AMR activity. Based on the high specificity of C4d positivity, it is considered equivalent to the serological proof of donor-specific antibody (DSA) for a diagnosis of AMR, although it is still recommended to test for DSA.
Chronic Allograft Arteriopathy
Chronic Allograft Arteriopathy is a feature of Chronic Active TCMR and Chronic Active AMR. It is defined as arterial intimal fibrosis with mononuclear cell infiltration in fibrosis and/or formation of neointima. The Banff Lesion Score cv is used to grade it, based on the extent of luminal occlusion in the most severely affected artery. Lack of prior biopsy-proven TCMR favours a diagnosis of Chronic Active AMR.12
Cortex
The outer part of the renal parenchyma, beneath the capsule and peripheral from the medulla, including the columns of Bertin. It is characterised by the presence of glomeruli and arteries.35
Donor-specific Antibody (DSA)
Circulating antibodies directed against donor human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I and/or class II and/or non-HLA antigens. For the definition and technical details see the recent and forthcoming consensus recommendations by The Transplantation Society.15-17 DSA are relevant for Banff Diagnostic Category 2 (AMR) diagnoses. For Active and Chronic Active AMR only DSA present at the approximate time of biopsy and against the current transplant are considered positive for the diagnosis; for Chronic AMR DSA against the current transplant present at or prior to the biopsy are considered.12
Fibrointimal Thickening, Arterial See ->Transplant Arteriopathy.
Glomerulonephritis
Recurrent or de novo glomerulonephritis can occur in renal transplant biopsies. The diagnosis is made by a combination of conventional histology, immunohistochemistry or immunofluorescence, electron microscopy and correlation with clinical data. It should be diagnosed under Banff Diagnostic Category 6, and can be used in combination with categories 2-5 and any other diagnosis from Category 6. The presence of glomerulonephritis precludes the use of Banff Lesion Score g as histologic evidence of acute tissue injury for the diagnosis of Active AMR and of Banff Lesion Score cg as evidence of chronic tissue injury in the diagnosis of Chronic Active or Chronic AMR.12
Haemorrhage, Tubulointerstitial
Extravasation of red blood cells into the tubulointerstitium. There is no special Banff Lesion Score for this lesion. Instead, the lesion is noted as an asterisk “*” attached to Banff Lesion Score v (e.g. v0* or v3*). It shares this coding with Infarct.5
Infarct
Zone of tissue which is non-viable due to insufficient blood supply. It qualifies as “necrosis” listed in the supplement of Banff 2015 and since Banff 19975 has been coded with an asterisk (*) behind the Banff Lesion Score v (e.g. v1*, v2*) accordingly.11 Infarcted areas must not be scored for Banff Lesion Score C4d.8
Infection
In the presence of Infection (Table 5, Banff 2017) Banff Lesion Score g>0 greater is required when using moderate microvascular inflammation (sum of Banff g+ptc≥2) as a criterion from Criteria Group 3 (antibody interaction with tissue) for a diagnosis of Active AMR or Chronic Active AMR.12 I.e. Banff Lesion Score ptc2 with Banff Lesion Score g0 is insufficient for this criterion when disease caused by infection of the transplant is present.
Interstitial Fibrosis
Banff Lesion Score ci for interstitial fibrosis was initially meant to describe the area fraction of fibrous tissue in the cortex only regardless of whether it represented fibrous tissue as the normal constituent of the renal cortex (considered to be 5%) or fibrous tissue within a cortical scar. Hence, a precise definition for individual patches of interstitial fibrosis in a scar has never been given. This purely morphometric approach runs counterintuitive to routine histopathological assessment for atrophic tubules separated by interstitial fibrosis in a tubulointerstitial scar. Guides for the assessment of Banff Lesion Score ci can be found in the main body of this manuscript.
Microvascular Inflammation, Moderate
Microvascular inflammation is scored by calculating the sum of the two Banff Lesion Scores g and ptc. Microvascular inflammation is considered moderate with [Banff Lesion Scores g + ptc] ≥2. In the presence of Acute TCMR, Borderline Changes or Infection such as Pyelonephritis, Banff Lesion Score g must be equal or greater than 1 in this calculation to fulfil the criteria for moderate microvascular inflammation.
Peritubular Capillary
Only capillaries within the renal cortex are peritubular capillaries (PTCs) which can be used for scoring peritubular capillaritis as in Banff Lesion Score ptc. Capillaries next to lymphoid follicles must be disregarded to avoid confusion with lymphatic vessels. Banff Lesion Score C4d can be scored not only in PTCs but also in medullary vasa recta.
Peritubular Capillary Basement Membrane Multilayering
Severe Peritubular Capillary Basement Membrane Multilayering (ptcml) is defined as “seven or more layers of basement membrane in one cortical peritubular capillary and five or more in two additional capillaries, avoiding portions cut tangentially“.12 Only Severe Peritubular Capillary Basement Membrane Multilayering is considered sufficient as one possible criterion for chronicity of AMR. This relative high threshold has been established because mild PTCML can be seen in other diseases like hypertension. In cases where electron microscopy (EM) is carried out in transplant biopsies, cortical peritubular capillary multilayering should be assessed and reported. The number of layers of basement membrane should be counted in the most affected PTC as well as in at least two additional PTCs. Tangentially cut PTC should be avoided. The biopsy report should state the number of PTC examined; the number of basement membrane layers in the 3 most affected PTC; and whether the Banff 2013 threshold for chronic ABMR (1 PTC with ≥7 layers + 2 PTC with ≥5 layers) is met. See also recommendations for performing EM cited from the Banff 2015 report under Banff Lesion Score cg for more detail.11
Pyelonephritis
Inflammation of the transplant parenchyma caused by bacterial or fungal infection, usually ascending from the bladder. This falls within the remit of Banff Diagnostic Category 6. As an -> Infection, the presence of Pyelonephritis has important bearings on the diagnosis of Active AMR and Chronic Active AMR, as then Banff Lesion Score g must be equal or greater than 1 to fulfil the criteria for -> Microvascular inflammation, Moderate ([Banff Lesion Score g + ptc] ≥2).12
Polyomavirus Nephropathy
Replicative infection of the kidney by polyoma virus as indicated by viral inclusions seen on histology, immunohistochemistry and/or electron microscopy. A Banff Working Group for Polyomavirus Nephropathy has developed and validated a respective scoring schema, which was presented at the meeting in 2017 and has been published recently. The percentage of tubules expressed in the Banff Lesion Score pvl and Banff Lesion Score ci yield the classification as 1,2 or 3.22 Polyomavirus nephropathy is included in Banff Diagnostic Category 6.
Scarred Cortical Parenchyma
Characterised by cortical tubular atrophy, usually but not always accompanied by interstitial fibrosis –see ->Tubular Atrophy. Banff Lesion Score i must not be scored in these areas, instead Banff Lesion Score i-IFTA is assessed in the areas.
Subcapsular Cortex
This term refers to areas immediately beneath the capsule, which may show areas of non-specific scarring or inflammation thought to be related to surgical ‘healing in’.1 The extent of the cortex that qualifies as “subcapsular” has not been more clearly defined in the Banff Classification. Banff Lesion Scores ptc7 and i11 must not be scored in these areas.
T Cell-mediated Rejection (TCMR)
The spectrum of TCMR is defined as Banff Diagnostic Category 4 which contains Acute TCMR Grade IA, IB, IIA, IIB, III as well as Chronic Active TCMR Grade IA, IB and II. Suspicious (Borderline) For Acute TCMR is the only diagnosis in Banff Diagnostic Category 3. Banff Diagnostic Categories 3 and 4 but can be rendered together for the combination of borderline with chronic active TCMT, or with other diagnoses from Categories 2, 5 and 6.
Thrombotic Microangiopathy, Thrombotic Microangiopathy In The Absence Of Any Other Cause
Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) can be caused by recurrent disease (usually atypical haemolytic-uremic syndrome), AMR, Calcineurin Inhibitor Toxicity (included in Banff Diagnostic Category 6) and other causes.36 If there is evidence of chronic TMA, Banff Lesion Score cg must not be used as a criterion for histological evidence of chronic tissue injury in the diagnosis of either Chronic Active AMR or Chronic AMR.12
Transplant Arteriopathy
Transplant Arteriopathy is defined as arterial fibrointimal thickening, also referred to as vascular fibrous intimal thickening, and is graded based on the extent of luminal occlusion in the most severely affected artery. Transplant arteriopathy is scored with the Banff Lesion Score cv. Features that suggest Chronic Active TCMR Grade II or Chronic Active AMR versus other causes such as conventional arteriosclerosis or hypertension are disruption of the elastica, inflammatory cells in the fibrotic intima, proliferation of myofibroblasts and/or foam cells in the expanded intima, formation of a neointima.11 However, it should be noted that bland but progressive intimal fibrosis may be associated with the presence of DSA.37
Transplant Glomerulopathy
Transplant glomerulopathy is defined as a Banff Lesion Score cg greater than 0, after the exclusion of chronic thrombotic microangiopathy, recurrent or de novo Glomerulonephritis. It is not synonymous to AMR, but is frequently associated with it.
Tubular Atrophy
Moderately atrophic tubules are defined as tubules having a diameter <50% of that of unaffected or minimally affected tubules on the biopsy, with wrinkling and/or thickening of the tubular basement membrane.5 Severely atrophic tubules are defined as tubules of diameter <25% of that of unaffected or minimally affected tubules on the biopsy, often with an undifferentiated- appearing, cuboidal or flattened epithelium (or in some cases even loss of epithelium with denudation of the tubular basement membrane), and pronounced wrinkling and/or thickening of the tubular basement membrane. This definition of severely atrophic tubules also includes very small, endocrine-like tubules with very narrow lumens, although the basement membranes of the latter may not be thickened.12 According to Banff 2019, severely atrophic tubules should be disregarded for Banff Lesion Scores t and t-IFTA.13
Banff-Kidney-2023-2